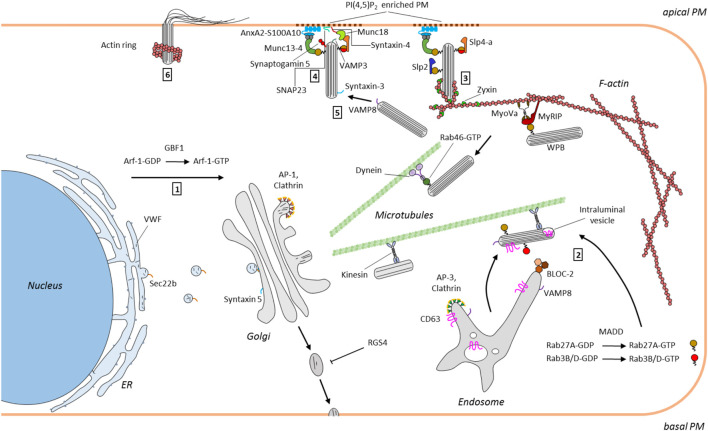
FIGURE 1.
Scheme depicting the WPB itinerary in endothelial cells. WPB formation is driven by VWF that is produced at the ER and trafficked to the Golgi (1). WPB that bud from the TGN in an AP-1 and clathrin dependent process are then transported to the cell periphery along microtubules. This is accompanied by the BLOC-2 and annexin A8 dependent transfer of endosomal components such as CD63 and VAMP8 to WPB (2). Maturing WPB acquire certain RabGTPases, e.g. Rab27A and Rab3B/D, the former required for linking WPB at the cortical actin cytoskeleton (via MyRIP/MyoVc) and supporting exocytosis (via Slp4-a) (3). Secretagogue induced tethering at and fusion with the PM requires docking factors, such as the annexin A2/S100A10/Munc13-4 complex and a SNARE-based fusion machinery and can also involve compound and cumulative events (3, 4 and 5). Finally, post fusion actin rings have been observed that support the full release of highly multimeric VWF (6). Mainly factors identified in the recent years have been included.