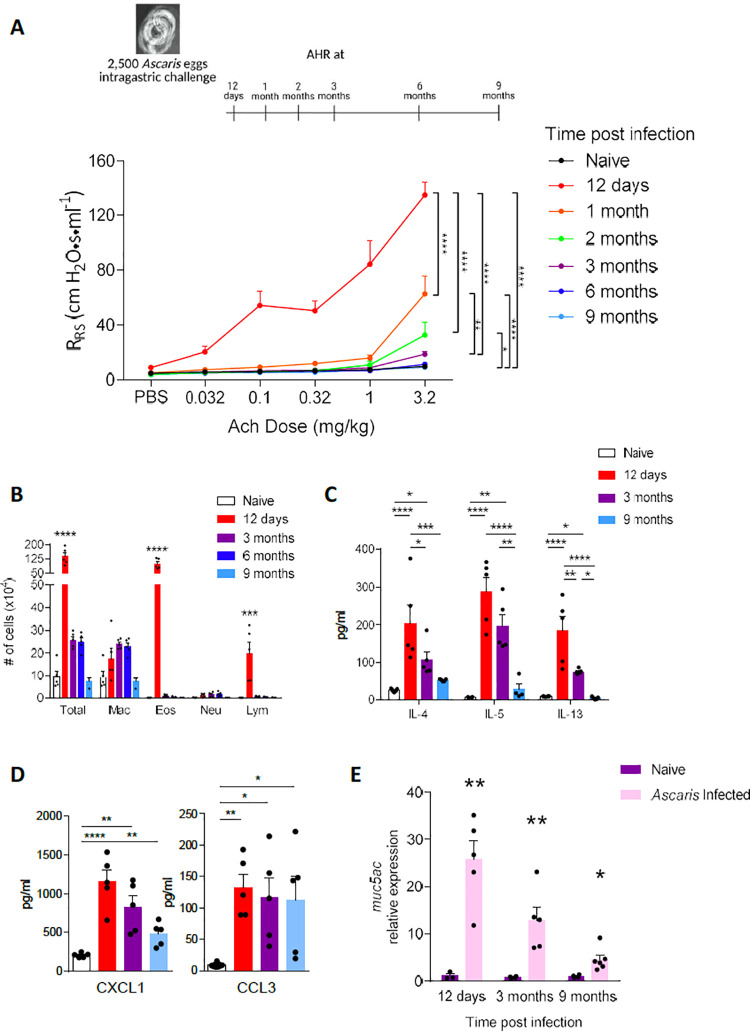
Fig 1. Ascaris induces long term pulmonary type-2 inflammatory pathology in mice.
BALB/c mice were challenged by oral gavage with 2,500 eggs of Ascaris once or phosphate buffered saline (PBS), and type-2 inflammatory pathology was assessed for both Ascaris-infected and PBS naïve mice at standard intervals post-infection (p.i.) as indicated on the timeline. A representative PBS naïve mouse group is displayed for each experiment as the values at each time interval remained unchanged across naïve groups (A) Respiratory system resistance (RRS) was assessed after intravenous injection of increasing doses of acetylcholine (Ach) to assesses airway hyperreactivity (B) Quantitation of cells from bronchoalveolar lavage fluid samples (mac: macrophages; eos: eosinophils; neu: neutrophils; lym: lymphocytes) to determine cellular composition over time (C) TH2 cytokines including Interleukin (IL)-4, IL-5, IL-13 and (D) chemokines C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 1 (CXCL1) and C-C motif chemokine ligand 3 (CCL3) quantitated by Luminex and ELISA from deaggregated lung supernatants (E) mRNA level of mucin5AC (muc5AC) from lungs post infection at standard intervals p.i.. (n≥5, mean ± standard error of the mean (S.E.M), n.s.: not significant, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test for multiple comparison. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments)