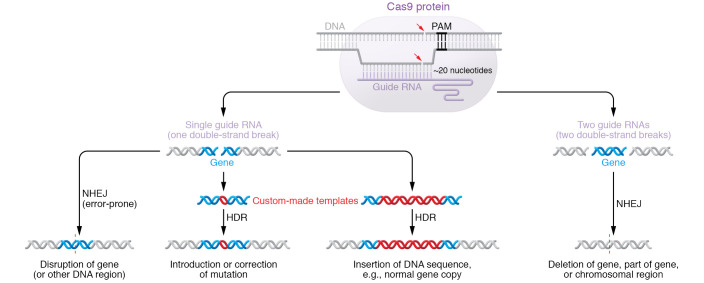
Figure 1. CRISPR/Cas9 nuclease editing.
The protospacer-adjacent motif (PAM) in the DNA and spacer sequence in the guide RNA direct CRISPR/Cas9 to a specific genomic site. There, it generates a double-strand break (indicated by red arrows pointing to DNA strands) that is repaired by one of two repair mechanisms: non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) or homology-directed repair (HDR). In NHEJ, free DNA ends are ligated together, which can restore the original DNA sequence or introduce insertions or deletions. This strategy is suitable for disrupting genes or non-coding elements in the genome. HDR enables more precise changes but requires the addition of a template, which reduces its efficiency. Adapted with permission from the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (58).