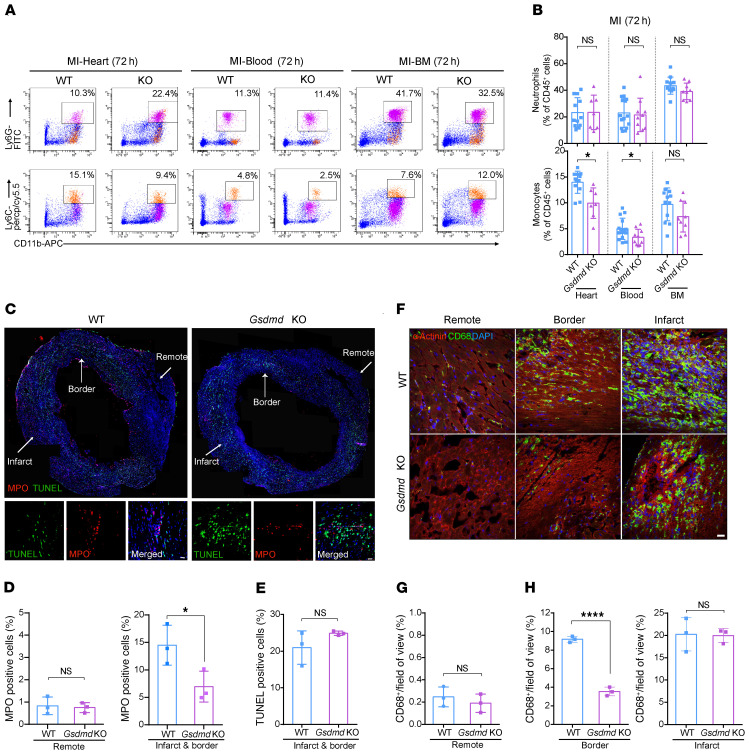
Figure 4. GSDMD is essential for recruitment of neutrophils/monocytes to the infarcted heart.
(A and B) Flow cytometric analysis and quantification of Cd11b+Ly6G+ neutrophils and Cd11b+Ly6C+ monocytes in the heart (left), blood (middle), or BM (right) from WT or Gsdmd−/− mice 72 hours after AMI (n = 7–15). (C) Immunofluorescence imaging and magnification for MPO (red), TUNEL (green), and DAPI (blue) on heart sections from WT or Gsdmd−/− mice 24 hours after AMI. Scale bar: 20 μm. (D and E) Quantification of ratios of MPO+ or TUNEL+ cells of heart sections from WT or Gsdmd−/− mice. Each value was averaged from the values of 7 fields of view from the same mouse (n = 3 per group). (F) Immunofluorescence imaging of heart sections from WT or Gsdmd−/− mice 3 days after AMI showing α-actinin (red), CD68 (green), and DAPI (blue). Representative fields of remote zone, border zone, and infarct zone are presented. Scale bar: 20 μm. (G and H) Quantification of CD68+ area proportion in the field of view in remote zone (G) and border and infarct zones (H) of heart sections from WT or Gsdmd−/− mice. Each value was averaged from the values of 5 fields of view from the same mouse (n = 3 per group). Data are presented as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; ****P < 0.0001 by multiple 2-tailed Student’s t test (B) or unpaired, 2-tailed Student’s t test (D, E, G, and H). NS, not significant.