Figure 2.
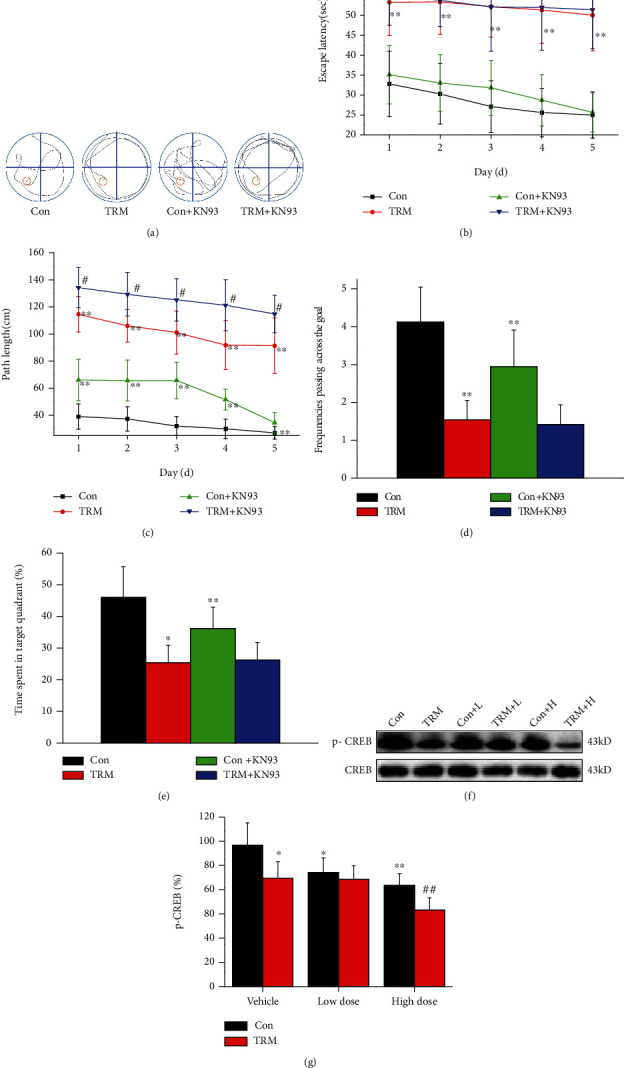
CaMKII inhibition enhances learning and memory impairment in the hippocampal neurons of Wistar and TRM rats. (a) The route trajectory in the hippocampus of Wistar rats, TRM rats, KN93- (high dose) treated Wistar rats, and KN93-treated (high dose) TRM rats. (b) The escape latency in Wistar rats, TRM rats, KN93-treated (high dose) Wistar rats, and KN93-treated (high dose) TRM rats as observed by employing the Morris water maze assessment. (c) The path length in Wistar rats, TRM rats, KN93-treated (high dose) Wistar rats, and KN93-treated (high dose) TRM rats in the navigation test of the Morris water maze. (d, e) Data analysis of the frequencies passing across the goal and the time in the target quadrant in Wistar rats, TRM rats, KN93-treated (high dose) Wistar rats, and KN93-treated (high dose) TRM rats using the Morris water maze. (f, g) Representative protein bands and data analysis of p-CREB proteins in the hippocampus of Wistar rats, TRM rats, KN93-treated (low dose) Wistar rats, KN93-treated (low dose) TRM rats, KN93-treated (high dose) Wistar rats, and KN93-treated (high dose) TRM rats. ∗p < 0.05, compared with the control Wistar group; #p < 0.05, compared with the control TRM group; ∗∗p < 0.01, compared with the control Wistar group; ##p < 0.01, compared with the control TRM group.
