Figure 6.
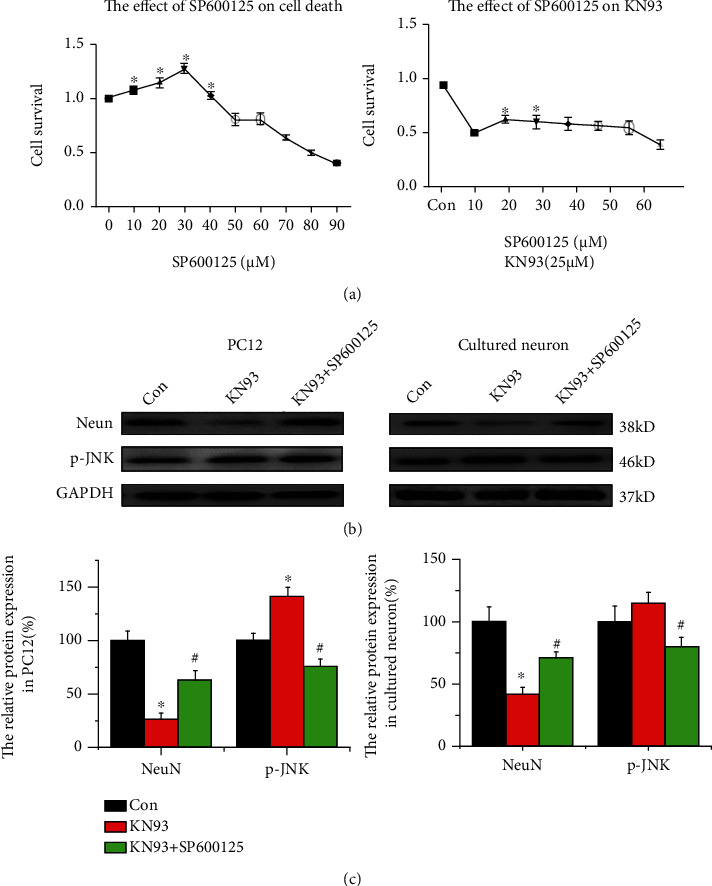
The p-JNK signaling pathway contributes to KN93-induced neuronal death. (a) The concentration-dependent curve of KN93-induced cytotoxicity shows treatment with the 0, 10, 20, 30, and 40 μM p-JNK inhibitor (SP600125) for 24 h after KN93 administration. (b, c) Representative protein bands and analysis of data for p-JNK and NeuN in control groups, KN93 groups, and KN93 + sp600125 groups of PC12 cells and primary hippocampal neurons. ∗p < 0.05, compared with the control group; #p < 0.05, compared with the KN93 group.
