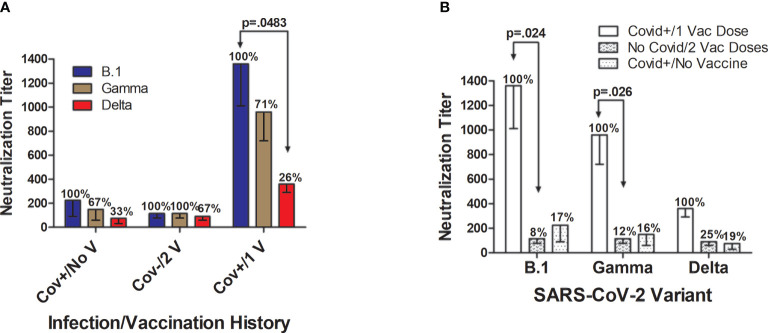
Figure 4.
Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 infectivity according to viral variant and subject infection and BNT162b2 vaccination history. (A) In unvaccinated individuals hospitalized with SARS-CoV-2 (n=8), mean neutralization effectiveness against the B.1 strain (set as 100%; titer=225 ± 135 fold dilution) was reduced by 33% against the Gamma variant (titer=150 ± 90) and by 67% against the Delta variant (titer=75 ± 45). In SARS-CoV-2-naïve subjects (n=8) who received the 2-dose BNT162b2 vaccination series, neutralizing effectiveness was similar against the three SARS-CoV-2 variants with inhibitory activity against the B.1 strain (set at 100%; titer=115 ± 39) maintained at 100% against the Gamma variant (titer=115 ± 39), and modestly 23% lower against the Delta variant (titer=90 ± 30). By far the strongest neutralizing ability was elicited in volunteers (n=3) who had previously been diagnosed with and recovered from Covid-19 and then received a single BNT162b2 vaccine dose. In this Covid+/1 Vaccine Dose group, the average maximal neutralizing titer against the B.1 strain (set at 100%; titer=1360 ± 349) were reduced by 29% against the Gamma variant (titer=960 ± 240; p>0.05) and by 74% against the Delta variant (titer=360 ± 69; p=0.048). (B) Individuals who had previously recovered from Covid-19 and then received a single vaccine dose developed significantly higher neutralization titers against B.1 and Gamma strains when compared to Covid-naïve individuals who received 2 vaccine doses. Neutralization of the Delta variant was also numerically 4-fold higher in Covid+/1 Vaccine Dose subjects versus Covid-naïve/2 Vaccine Dose subjects, and 5-fold higher than in unvaccinated individuals who were hospitalized for Covid-19, but these differences did not attain statistical significance. Neutralization capacity of the plasma of subjects hospitalized with Covid-19 did not remarkably differ from neutralization by Covid-naïve individuals who received the both vaccine doses, for all SARS-CoV-2 strains studied. Shown are mean values ± SEM.