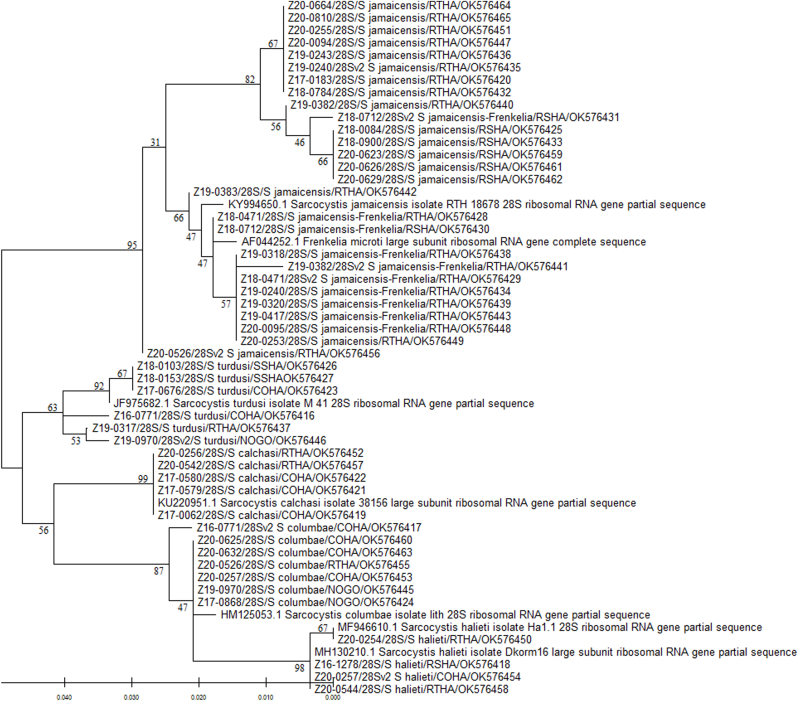
Fig. 3.
Phylogenetic tree based on 28S rRNA sequences of Sarcocystis spp. obtained from raptor intestinal samples and reference sequences available in GenBank. The phylogenetic relationships were determined by the Maximum Likelihood method using MEGA-X version 10.2.6 (Kumar et al., 2018). Numbers above or below nodes represent bootstrap confidence values from 500 replicates. The distances were computed using the Tamura-Nei model (Tamura and Nei, 1993). Branch lengths are proportional to sequence divergence and relate to the scale bar (bottom left). GenBank reference sequences are labeled by their accession number and associated information. Raptor sequences are labeled by animal identification number, region amplified (28S), Sarcocystis spp. with the highest homology found by BLASTn, 4-letter alpha-code for the raptor species common name, and NCBI accession number. COHA: Cooper's hawk (Accipiter cooperii), NOGO: northern goshawk (A. gentilis), RSHA: red-shouldered hawk (Buteo lineatus), RTHA: red-tailed hawk (B. jamaicensis), SSHA: sharp-shinned hawk (A. striatus). Note the Eumonospora henryae-like sequence was not included in the analysis. Detailed information for each bird and sequence is presented in Supplementary Table 1.