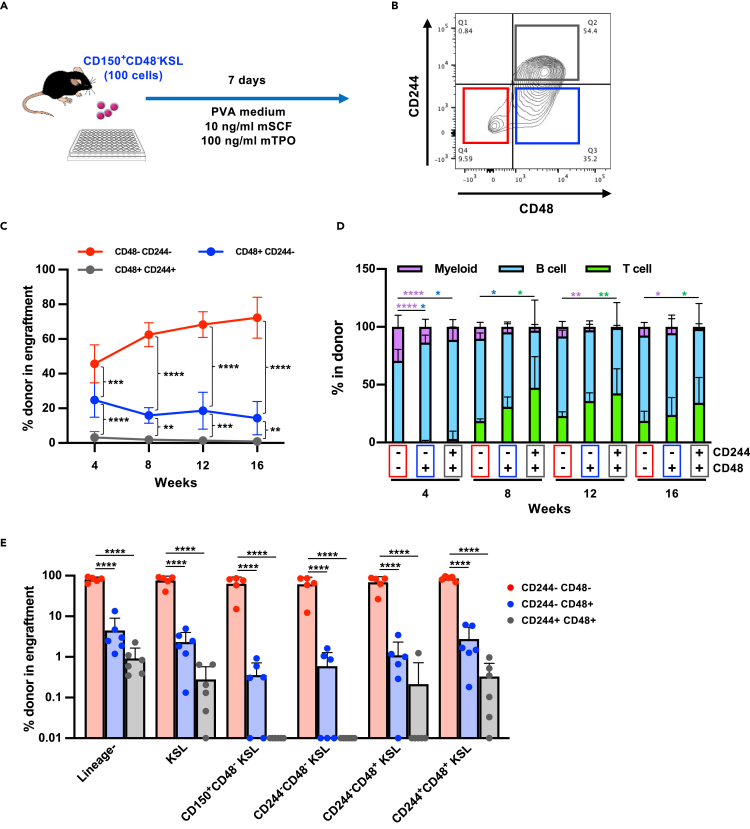
Figure 6.
CD244 expression distinguishes functionally distinct subpopulations after in vitro culture in PVA medium
(A) Experimental design of the in vitro culture experiment. One hundred CD48−KSL cells were sorted from BM of young mice and cultured in PVA containing medium (Wilkinson et al., 2019) supplemented with 10 ng/mL mSCF and 100 ng/mL hTPO for 7 days.
(B) Expression patterns of CD244 and CD48 on the cell surface of KSL cells after in vitro culture in PVA medium. A representative FACS plot on KSL population is shown.
(C) Competitive reconstitution assay. After 7 days’ culture, three subpopulations were sorted and 500 of CD244−CD48−KSL cells, CD244−CD48+KSL cells, or CD244+CD48+KSL cells were separately transplanted into lethally irradiated recipient mice with 2 × 105 total BM cells. Chimerism was monitored by analyzing PB every month. Significance was calculated using one-way ANOVA at each time point. Mean ± SD from two independent experiments (n = 12) are displayed. ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001
(D) Lineage balance of donor-derived cells in the PB of recipient mice. Significance was calculated using one-way ANOVA at each time point. Mean ± SD from two independent experiments (n = 12) are displayed. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. Each color represents different lineages.
(E) Analysis of BM from engrafted mice after 16 weeks. Chimerism in each cell fraction is shown. Significance was calculated using one-way ANOVA within each population. Mean ± SD from two independent experiments (n = 5) are displayed. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.