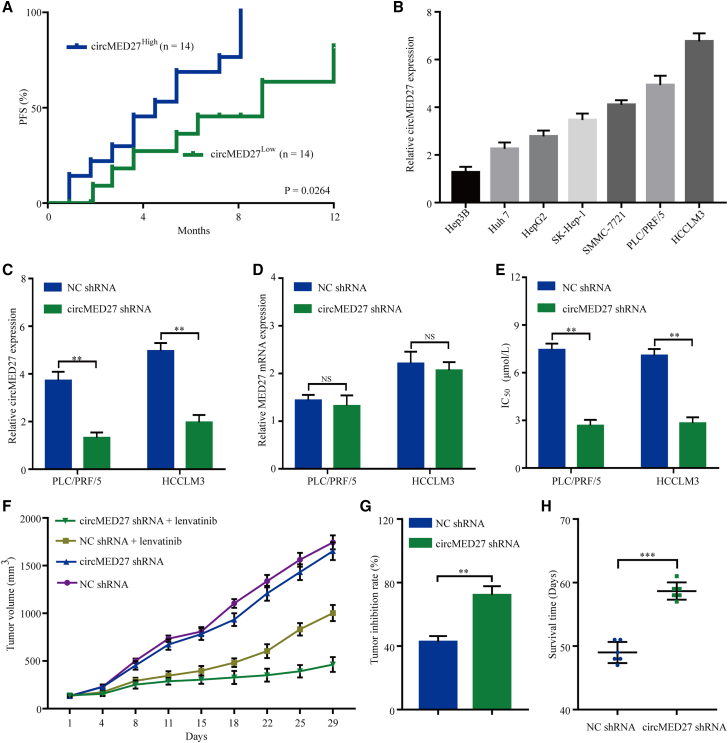
Figure 3.
circMED27 induces lenvatinib resistance in HCC cells
(A) Comparison of progression-free survival curves for patients with high and low circMED27 expressions that were treated with lenvatinib. (B) circMED27 expression in several HCC lines was examined using by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. (C) circMED27 expression in PLC/PRF/5 and HCCLM3 cell lines was modified by shRNA interference transfection. (D) MED27 mRNA expression in circMED27 knockdown HCC cells. (E) Reduced circMED27 expression in PLC/PRF/5 and HCCLM3 cells increased their sensitivity to lenvatinib. (F) Anti-tumor effect of lenvatinib on HCC xenografts in an established model (n = 6). (G) The data were expressed as the percentage of inhibition of tumor growth. (H) The survival time of mice bearing HCC subcutaneous xenografts received lenvatinib therapy. Data are represented as the mean ± SD. ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001.