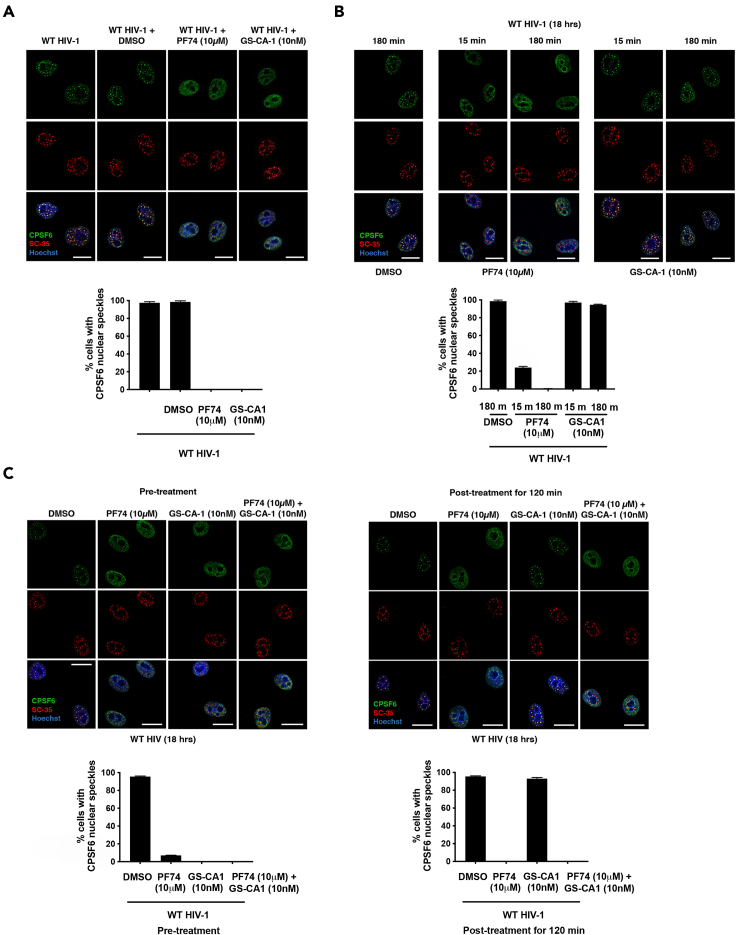
Figure 5.
PF74, but not GS-CA1, disaggregates preformed CPSF6 complexes in nuclear speckles by HIV-1 infection
(A) HeLa cells were infected with wild-type HIV-1-Luc virus pseudotype with VSV-G in the presence of PF74, GS-CA1, or DMSO as a vehicle control. Cells were incubated for 18 h at 37°C. Mean nuclear speckles ±SD are shown.
(B) HeLa cells were infected with wild-type HIV-1-Luc virus, and 18 h post-infection were treated with PF74, GS-CA1, or DMSO as a vehicle control for 15 or 180 min. Mean nuclear speckles ±SD are shown.
(C) Left panels: HeLa cells were infected with wild-type HIV-1-Luc virus in the presence of PF74, GS-CA1, PF74 and GS-CA1, or DMSO as a vehicle control. Cells were incubated for 18 at 37°C. Right panels: HeLa cells were infected with wild-type HIV-1-Luc virus, and at 18 h post-infection PF74, GS-CA1, PF74 and GS-CA1, or DMSO as a vehicle control were added for 120 min (A–C). After drug treatment, cells were immunostained using specific antibodies directed against CPSF6 (green) and SC35 (red). Nuclei were counterstained with Hoeschst (DNA). Mean nuclear speckles ±SD are shown. Scale bars, 5 μM.