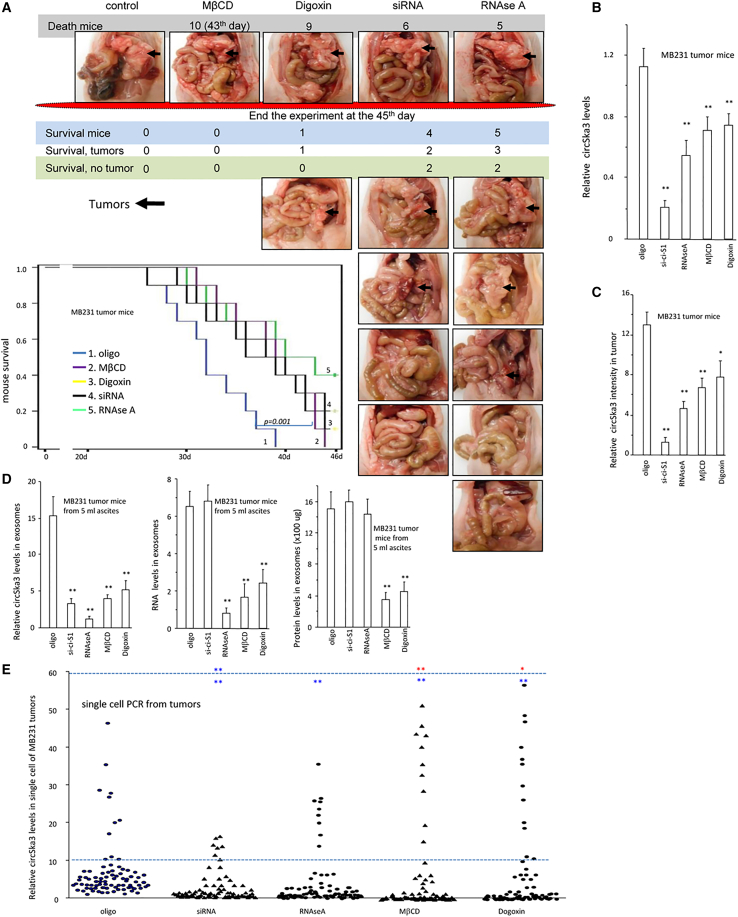
Figure 3.
circSKA3-containing exosomes potentiate tumor invasion
(A) After injection with MB-231 cells, CD-1 nude mice were also injected with control oligo, circSKA3 siRNA, RNAse A, MβCD, or Digoxin. The delivery of circSKA3 siRNA, RNAse A, MβCD, or Digoxin increased mouse viability significantly, relative to controls (log rank test, ∗∗p < 0.01). (B) PCR showed that the circSKA3 levels in the tumor tissues decreased when mice were injected with circSKA3 siRNA, RNAse A, Digoxin, or MβCD (n = 6). (C) ImageJ showed that the circSKA3 levels in the tumor tissues decreased when mice were injected with circSKA3 siRNA, RNAse A, Digoxin, or MβCD (n = 6). (D) circSKA3 levels in the exosomes decreased when mice were injected with circSKA3 siRNA, RNAse A, Digoxin, or MβCD (left). Total RNA levels in the exosomes of tumor tissues decreased when mice were injected with RNAse A, Digoxin, or MβCD (middle). Total exosomes of mouse ascites were lower when mice were injected with Digoxin or MβCD (right) (n = 5). (E) Single-cell PCR showed that approximately 8%–10% of cells (HIGH) expressed significantly higher levels of circSKA3 than other cells (LOW). Treatment with RNAse A, Digoxin, or MβCD did not affect the average levels of circSKA3 in the cells but decreased the circSKA3 levels in the LOW cells and increased the circSKA3 levels in the HIGH levels. Treatment with RNAse A only decreased circSKA3 levels in the LOW cells. Upper of the dotted line, HIGH expression; lower of the dotted line, LOW expression; red, upregulated; blue, downregulated. (n = 80), ∗ p<0.05; ∗∗ p<0.01; Error bars, SD.