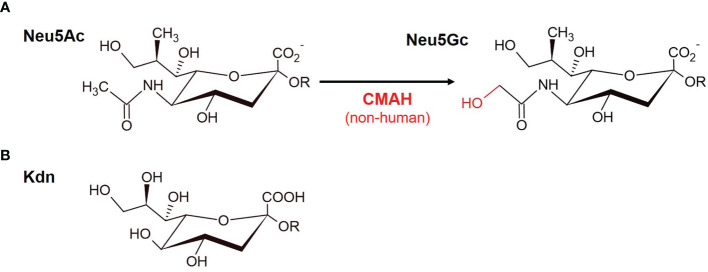
Figure 1.
Sialic acids. Sialic acids are nine-carbon monosaccharides. (A) The two main mammalian sialic acids N-acetyl neuraminic acid (Neu5Ac) and N-glycolylneuraminic acid (Neu5Gc) are shown. Neu5Gc is derived from Neu5Ac and differs by one oxygen atom in the N-glycolyl group, which is added by the enzyme cytidine monophosphate N-acetylneuraminic acid hydroxylase (CMAH) in the cytosol. Humans have an inactivating mutation of the CMAH gene and therefore they lack this enzymatic activity. (B) Kdn (2-keto-3-deoxy-D-glycero-D-galacto-nononic acid), which is more common among lower vertebrates and bacteria (see text).