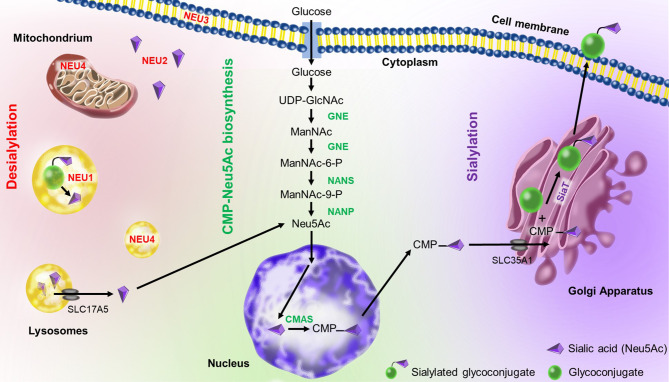
Figure 2.
Sialic acid metabolism in humans. CMP-Neu5Ac mostly occurs in the cytoplasm except of the CMP-sialic acid synthase (CMAS)-mediated reaction which takes place in the nucleus. UDP-GlcNAc-2 epimerase (GNE) synthesizes N-acetylmannosamine (ManNAc) in two steps. Then, Neu5Ac synthase (NANS) generates ManNAc-9-P, which is then dephosphorylated by Neu5Ac-P-phosphatase (NANP) to generate free sialic acid in the cytoplasm. The free sialic acid can enter the nucleus to be linked to CMP (cytidine-5’-monophosphate). The CMP-Neu5Ac is transferred to the Golgi apparatus via SLC35A1 transporter (solute carrier family 35 member A1), where it is used as a substrate for sialylation by different sialyltransferases (SiaT). Sialylated glycoconjugates are then exported to the cellular membrane or secreted. They can also be broken down by various neuraminidases (NEU1-4) present in different cellular localizations. The released sialic acid can reenter the biosynthesis pathway. Illustration by Aldona von Gunten.