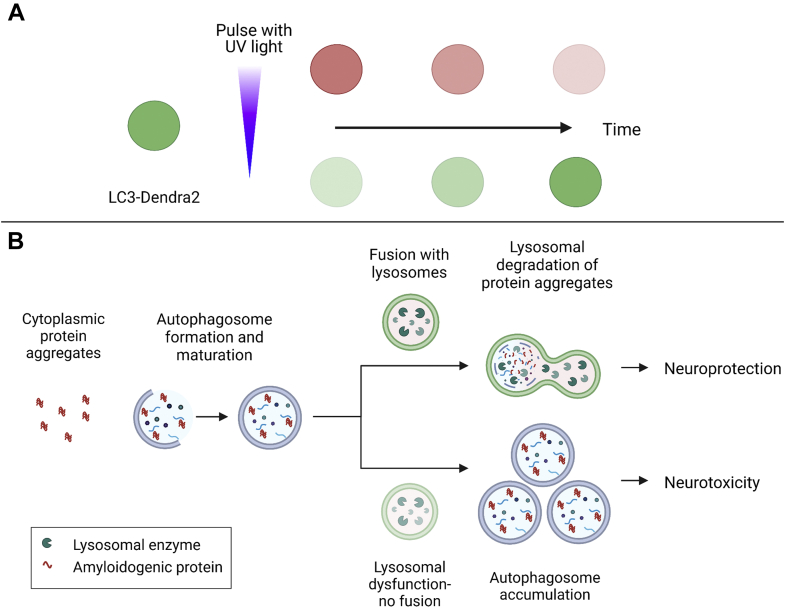
Figure 1.
The neuroprotective potential of autophagy inducers depends on the efficiency of autophagic flux.A, schematic of the experimental design used by Safren et al. to identify autophagy modulators. Dendra2-LC3 undergoes photoconversion, resulting in a switch from green to red fluorescence, in cells exposed to UV light. Red Dendra2-LC3 can then be imaged over time to monitor autophagic flux, whereas the green fluorescent protein can be imaged to monitor autophagosome formation. B, schematic illustrating different outcomes of autophagy induction depending on the status of autophagic flux. Cytoplasmic protein aggregates can be engulfed by an autophagosome that subsequently fuses with a lysosome, resulting in aggregate degradation and alleviation of neurotoxicity (upper pathway). In cells with downstream autophagic impairment (e.g., because of lysosomal defects that preclude autophagosome-lysosome fusion), autophagy induction results in a buildup of autophagosomes and exacerbation of neurotoxicity (lower pathway). Created with BioRender.com.