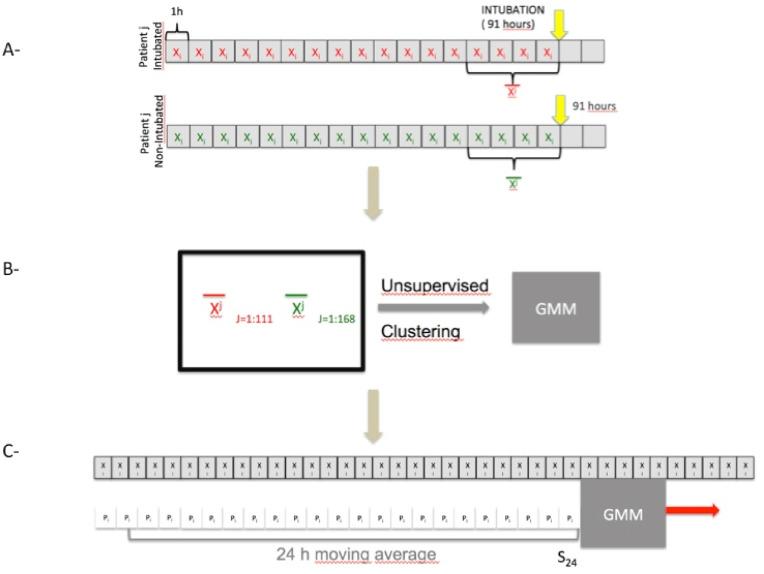
Fig. 1.
General Principles: A-The SpO2 and BF signals are used to calculate a state vector representing the patient's respiratory status every hour. This state vector is averaged over the last 4 h before intubation. We set a fictitious date of intubation for patients who were not intubated, which is 91 h after admission (91 h the average date of intubation for patients). The state vector is also averaged over the last 4 h prior to this fictitious intubation date. B- All state vectors of the 279 patients are provided to an unsupervised clustering algorithm (GMM). We compared the performance of this algorithm to the actual classification. C- The algorithm calculates the probability of intubation in 4 h every hour. However, this prediction is often distorted by brief periods of instability. This probability is therefore averaged over 24 h.