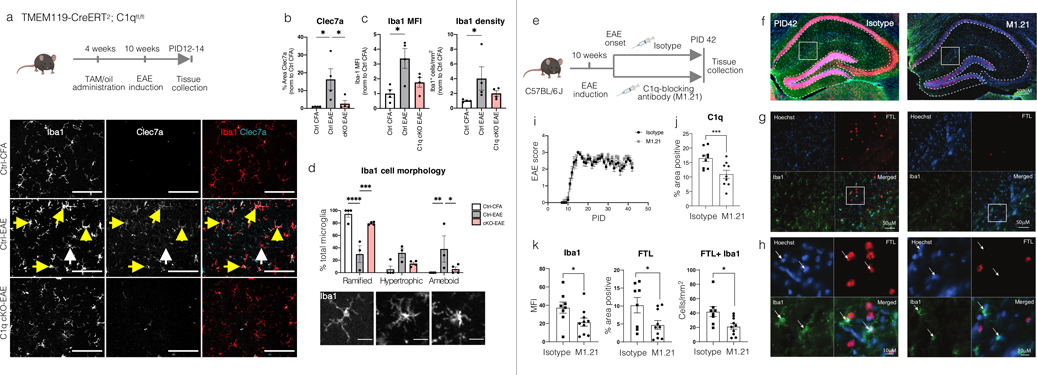
Extended Data Fig.10. C1q mediates microglia activation in mouse EAE.
Iba1+ cells in microglia-specific C1q cKO with EAE appear less reactive.
(a) Visual thalamus was immunostained at PID12-14 for Iba1 (microglia/macrophages) and Clec7a (disease-associated microglia). Yellow arrows denote Iba1+Clec7a+ cells, white arrows Iba1+Clec7a- cells. Scale bar=100μm.
(b–c) Clec7a decreased in cKO mice with EAE compared to Ctrl-EAE littermates. The density of Iba1+ cells and Iba1 MFI was attenuated to control values in cKO-EAE mice. *p<0.05, by one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s posthoc test (b) or Kruskal-Wallis test and Dunn posthoc test (c).
(d) Iba1+ cells were morphologically characterized into 3 categories (representative images in the panel below the quantification, scale bar=20 μm). Iba1+ cells in cKO-EAE mice were indistinguishable from CFA controls. cKO-EAE showed more ramified Iba1+ cells and fewer amoeboid cells compared to Ctrl-EAE littermates. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001 by two-way ANOVA and Tukey’s posthoc test. Error bars: SEM.
Anti-C1q treatment reduces expression of FTL and Iba1 in chronic EAE.
(e) Experimental paradigm (twice weekly treatment with isotype control or C1q-blocking antibody (M1.21) from EAE onset until PID42).
(f) Representative images of FTL and Iba1 immunostaining; higher magnifications (g–h). White arrows: Iba1+ cells.
(i) EAE scores for each treatment arm.
(j–k) Quantification of the expression of C1q, FTL, and Iba1 in hippocampal WM (outlined with the dashed line in panel f) and count of Iba1+FTL+ cells. Student t-test, p*≤0.05, ***≤0.001. Error bars: SEM.
EAE=experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis; cKO=conditional knock out; TAM=tamoxifen; FTL=ferritin light chain; MFI= mean fluorescent intensity; PID=post-immunization day; SEM=standard error of the mean.