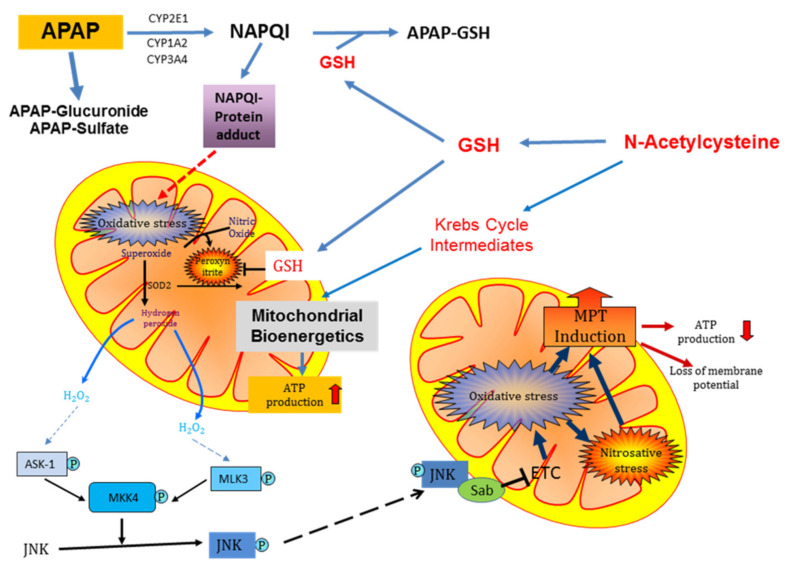
Fig. (3).
Schematic of the metabolism of acetaminophen by the hepatocyte and mechanism of action of N-acetylcysteine as an antidote to acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in overdose.
APAP, acetaminophen; ASK, apoptosis signal-regulating kinase; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; CYP, cytochrome P450; GSH, glutathione; JNK, c-jun N-terminal kinase; MLK, mixed-lineage kinase; MPT, mitochondrial permeability transition; NAPQI, N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine; Sab, SH3 domain-binding protein that preferentially associates with Btk; SOD, superoxide dismutase. (A higher resolution / colour version of this figure is available in the electronic copy of the article).