Table 1.
Structures of tacrine, donepezil and rivastigmine derivatives and their biological activities.
| S. No. | Structure | Additional Functions | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
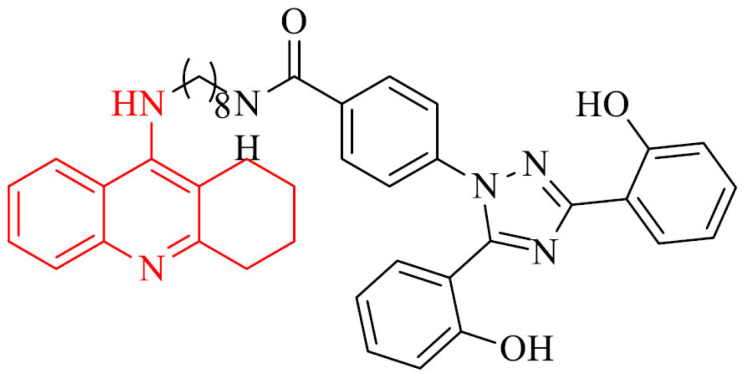
|
Antioxidant activity, protective properties against the injury caused by H2O2 | [81] |
| 2 |
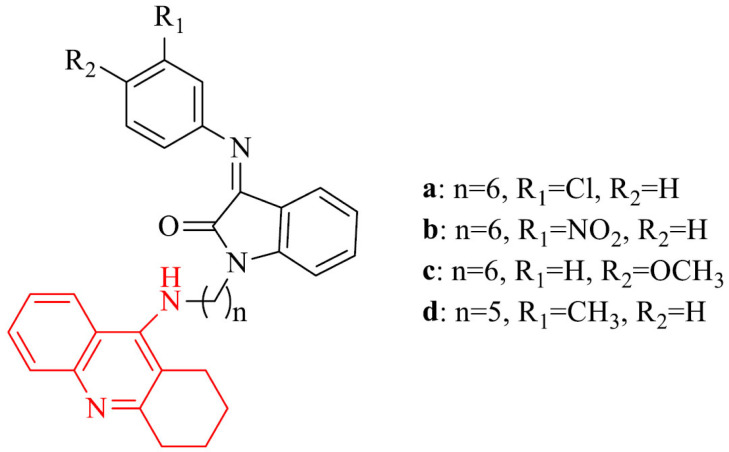
|
2a-d: excellent metal chelating properties. 2a,b: inhibitory potency against AChE-induced Aβ aggregation | [82] |
| 3 |
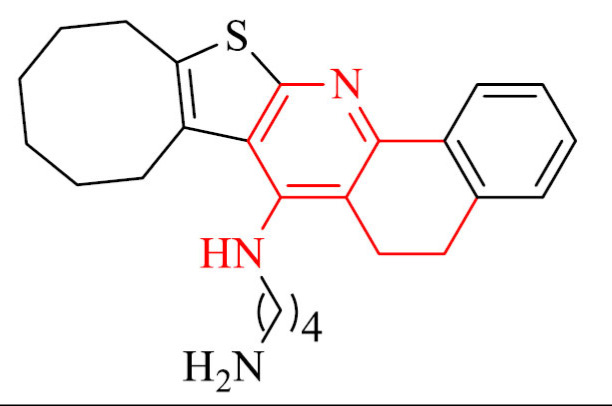
|
Promising in vivo AChE inhibition profile |
[83] |
| 4 |
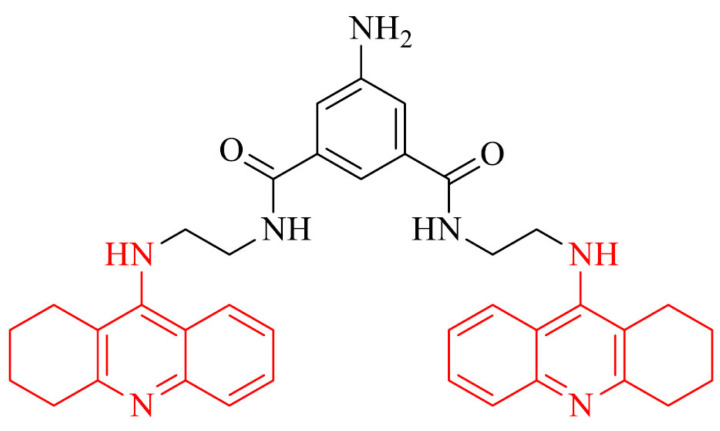
|
Inhibitory potency against PAS and AChE-induced Aβ aggregation, ability to induce S-phase post-treatment | [84] |
| 5 |
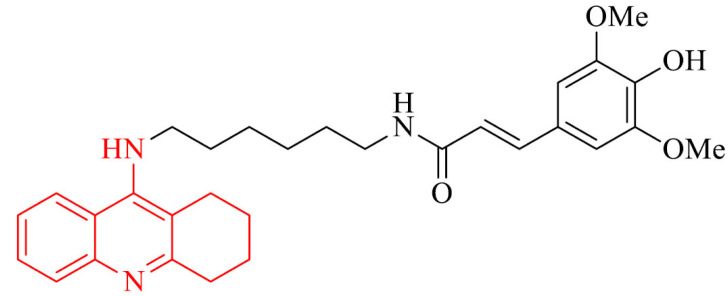
|
Inhibitory potency against Aβ self-aggregation at the level of 47% at 20 µM, antioxidant properties towards PC12 cells from CoCl2-damage | [85] |
| 6 |
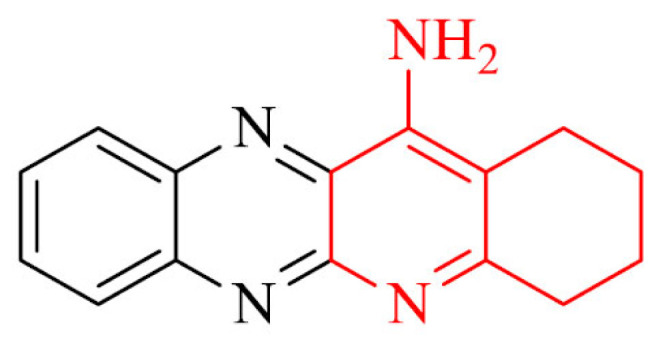
|
Neuroprotective activity towards SH-SY5Y cells against rotenone plus oligomycin-A or okadaic acid | [86] |
| 7 |
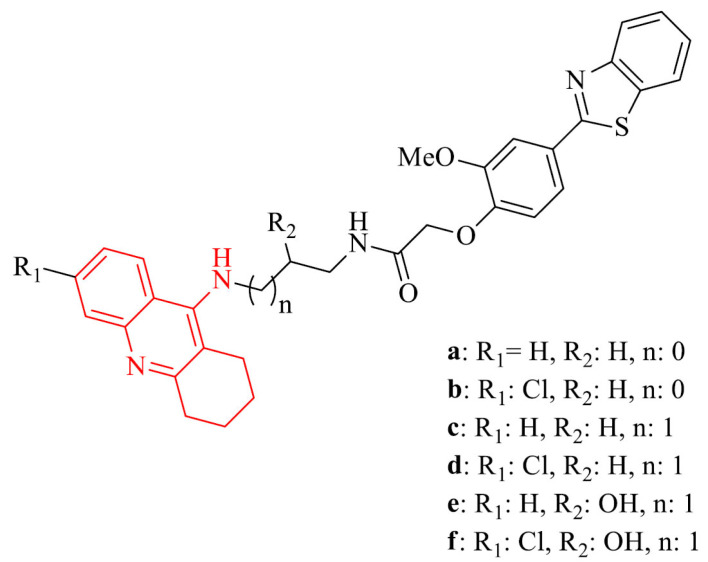
|
7b,c,f: neuroprotective activity on SH-SY5Y cell line | [88] |
| 8 |
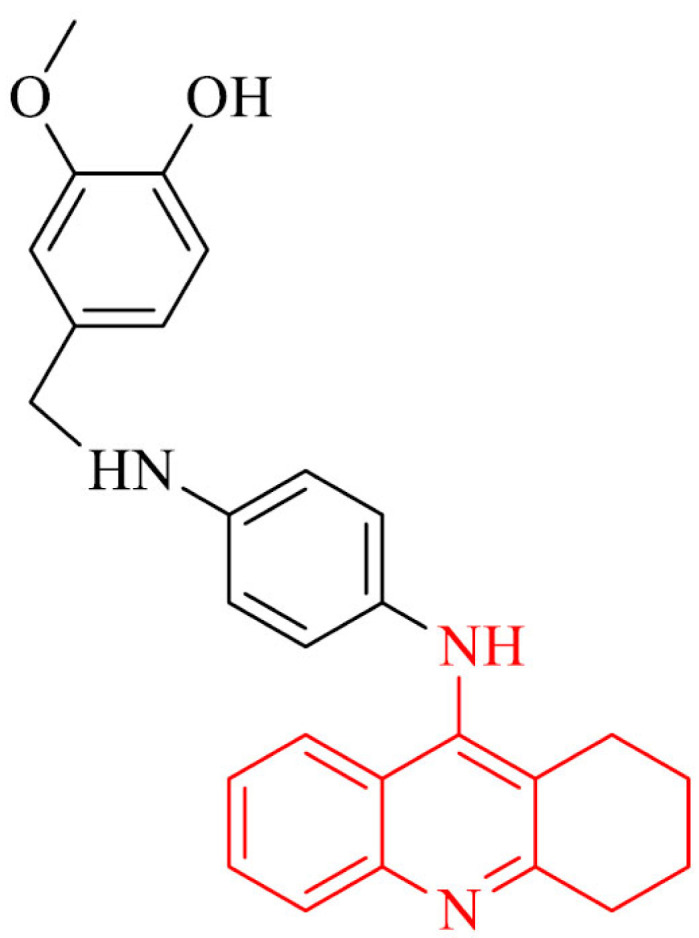
|
Antioxidant properties, inhibition of Aβ1-42 aggregation, neuroprotection of SH-SY5Y in the presence of H2O2 | [89] |
| 9 |
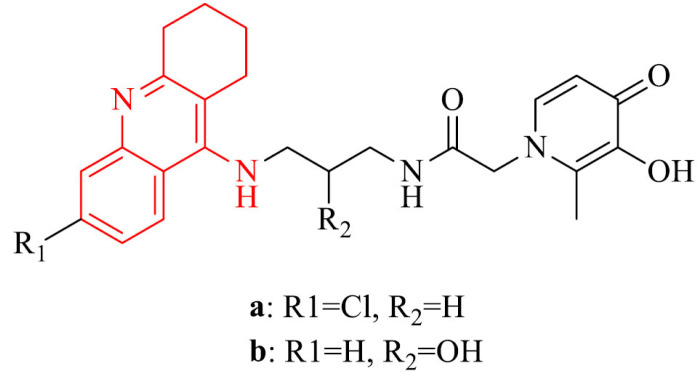
|
Inhibition of self-/Cu-induced Aβ aggregation, radical scavenging capacity and metal chelating properties (Fe, Cu, Zn), neuroprotection in SH-SY5Y cells treated with Aβ1-42 ascorbate/iron stressors | [96] |
| 10 |
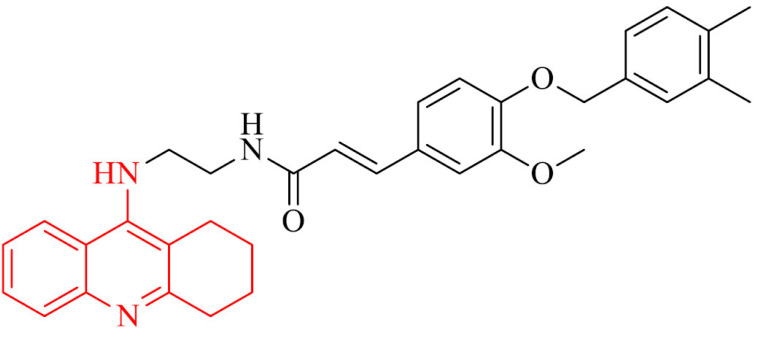
|
Inhibition of Aβ self-aggregation amelioration, the impairment of memory in mice models treated with scopolamine in the Morris water maze test | [97] |
| 11 |
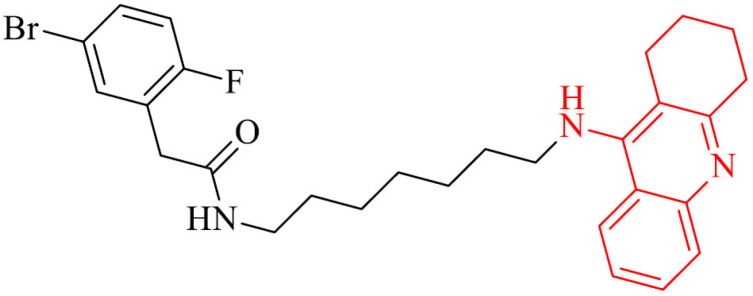
|
Inhibition of Aβ aggregation | [100] |
| 12 |
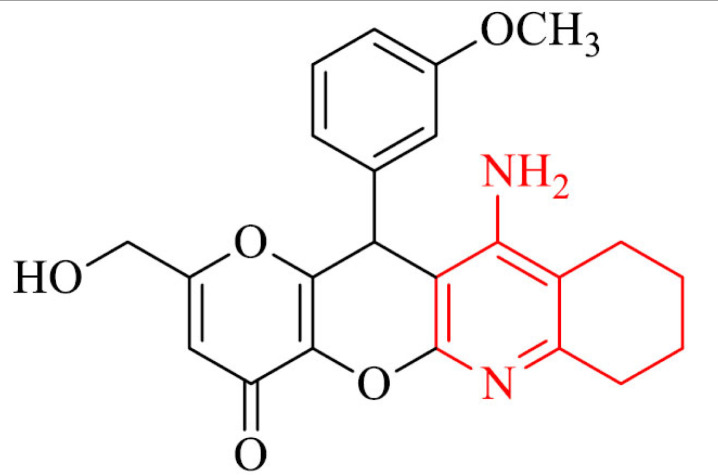
|
Antioxidant activity and neuroprotection against Aβ1-40 in SH-SY5Y cells | [101] |
| 13 |
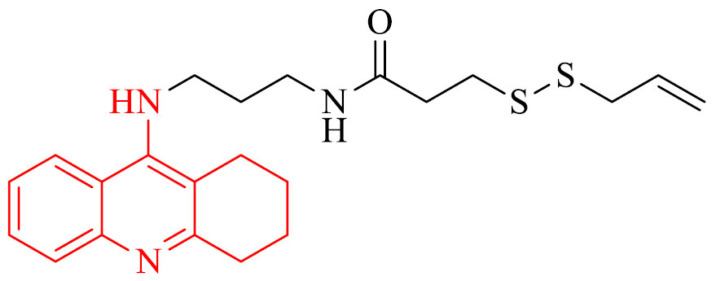
|
Improvement of cognitive and locomotor activity in a mouse model with AD in the step-through test and open field test, an increase of the amount of H2S in hippocampus, decrease mRNA expression of the proinflammatory cytokines, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β and increase synapse-associated in the hippocampus of tested mice | [108] |
| 14 |
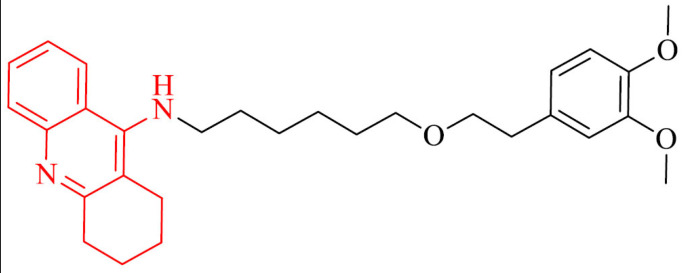
|
Inhibition of Aβ42 self-aggregation, neuroprotection in rats neurons in a serum and K+ deprivation model | [111] |
| 15 |
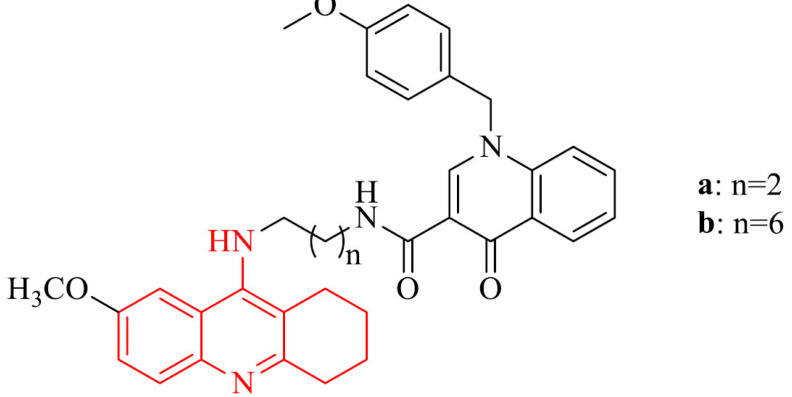
|
Ability to cross the BBB in vitro | [120] |
| 16 |
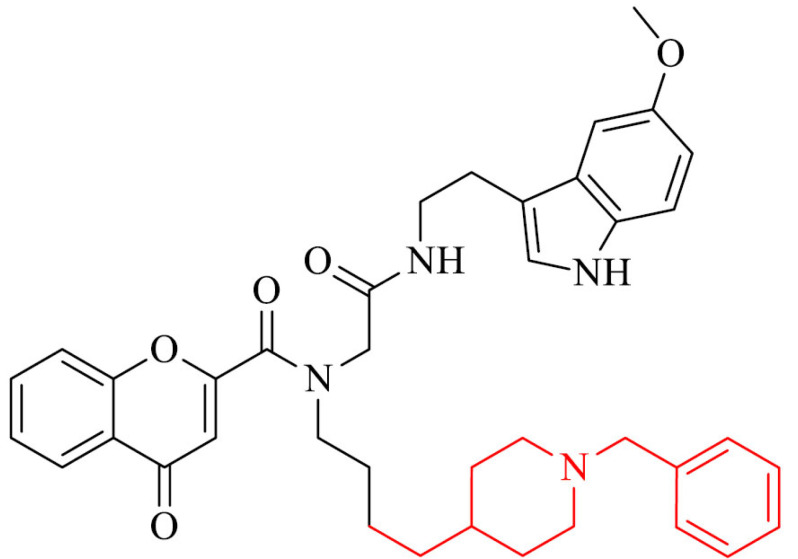
|
Inhibition of hMAO A, and MAO-B, strong antioxidant properties |
[127] |
| 17 |
|
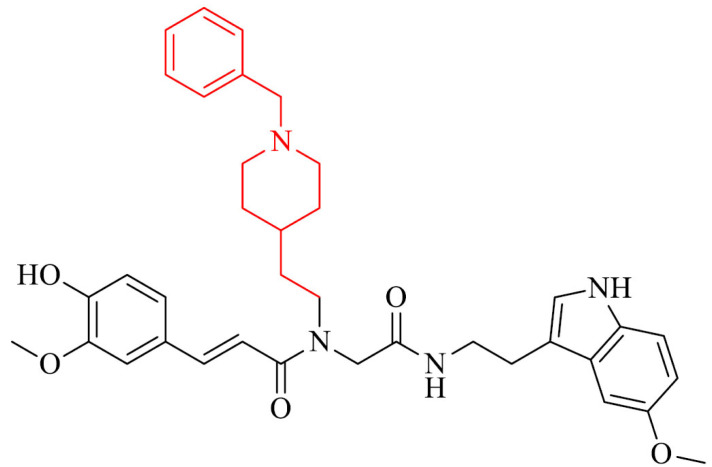
Strong antioxidant effect with the oxygen radical absorbance capacity | [129] |
| 18 |
|
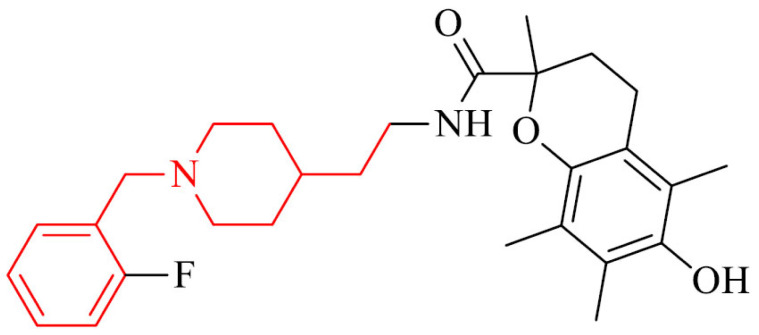
Inhibition of MAO-B and Aβ1−42 aggregation, antioxidant effect, ability to chelat Cu2+ ions, to protect PC12 cells from oxidative stress caused by H2O2, rotenone, and oligomycin-A, to protect BV-2 cells from LPS-Stimulated Inflammation, improvement of cognition and spatial memory against scopolamine-induced acute memory deficit, D-galactose (D-gal) and AlCl3 induced chronic oxidative stress in mice model without acute toxicity and hepatotoxicity, ability to cross the BBB in vitro |
[130] |
| 19 |
|
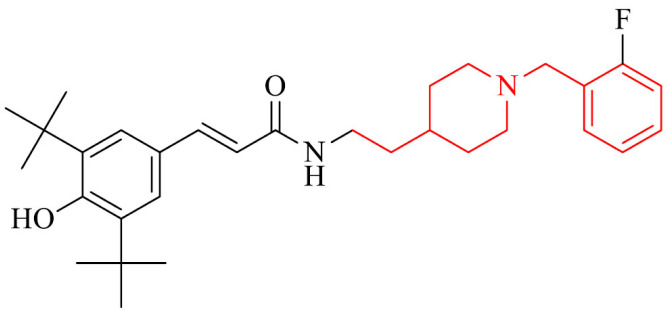
Inhibitory activity against hMAO-B, self-induced and hAChE-induced Aβ aggregation, antioxidant properties, the neuroprotective effects on PC12 cells treated with H2O2 and against LPS-stimulated inflammation on BV-2 cells, ability to cross the BBB in vitro, good liver metabolic stability in RLM, dose-dependently reversed scopolamine-induced memory deficit in mice model but without acute toxicity | [131] |
| 20 |
|
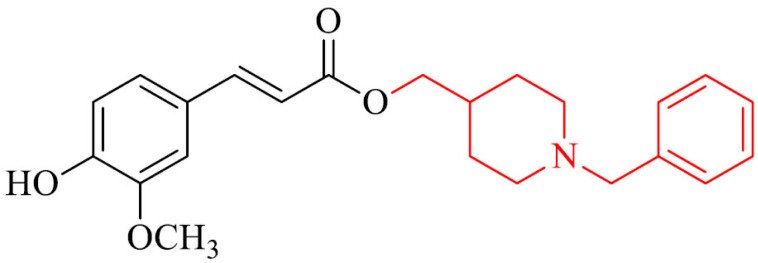
Anti-inflammatory properties in vivo in mice model, antioxidant activity in SH-SY5Y cell line and ability to chelate Cu2+ and Fe2+ ions, protection of SH-SY5Y cells against the late neuronal death caused by Aβ1-42 oligomers | [132] |
| 21 |
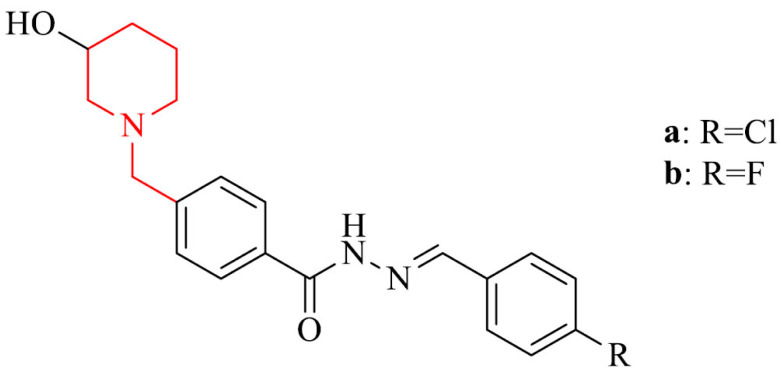
|
ADME profile in silico, anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective activity against AβO-induced neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in vitro in THP-1 cells and in vivo in mice model | [135] |
| 22 |
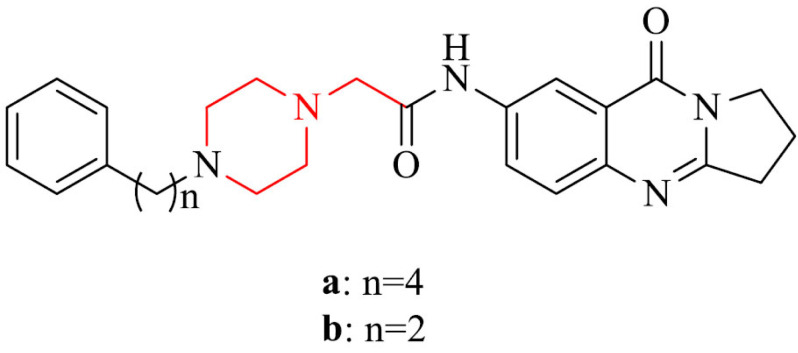
|
Inhibitory activity against BACE1 and Aβ1−42 aggregation, neuroprotective properties against Aβ1−42-induced damage in SH-SY5Y cells |
[139] |
| 23 |
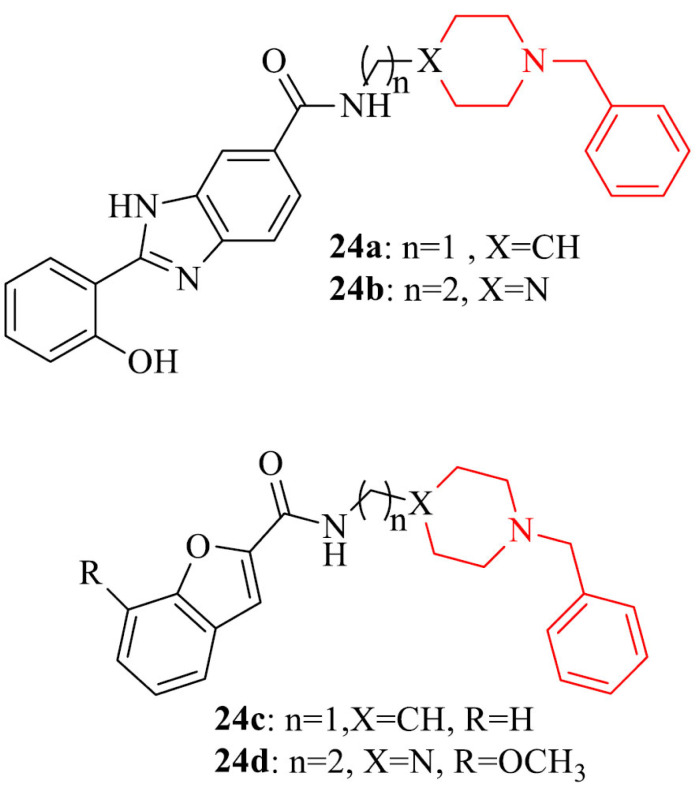
|
Inhibitory activity against Aβ self-aggregation and Cu2+-induced Aβ aggregation, ability to protect SH-SY5Y cells from the Aβ-induced toxicity | [141] |
| 24 |
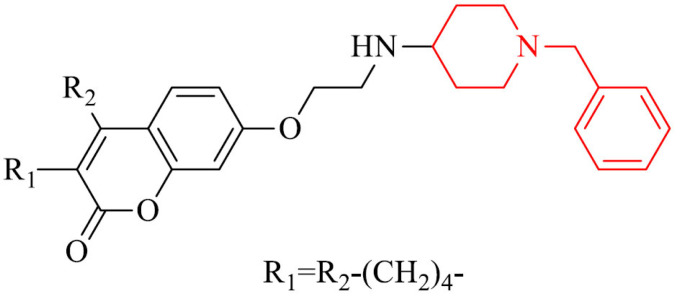
|
Inhibitory potency against MAO-B, ability to cross the BBB in vitro | [143] |
| 25 |
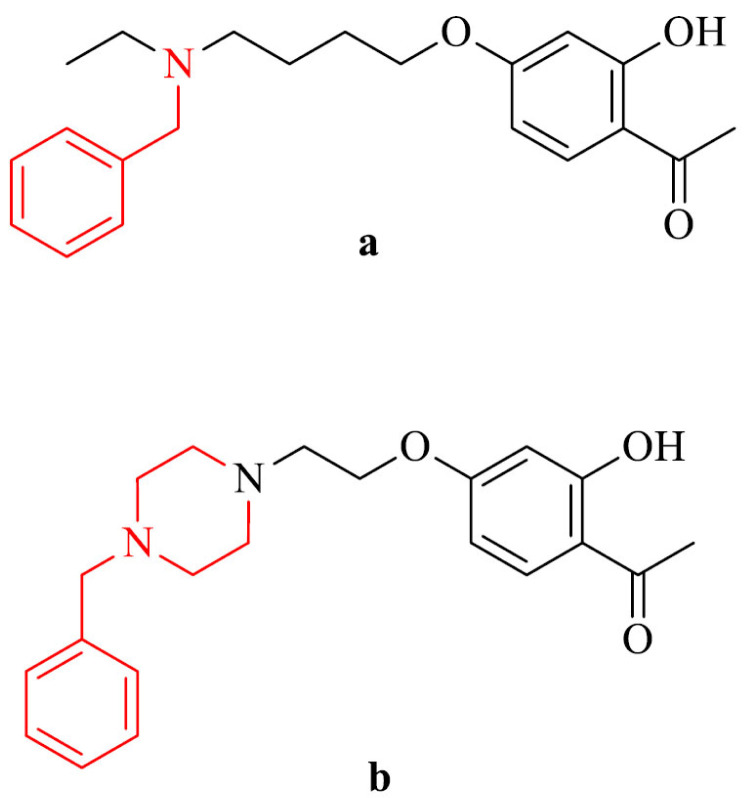
|
Selective Cu2+ chelator in a 1:1 ratio, ability to cross the BBB in vitro, activity against MAO-B | [144] |
| 26 |
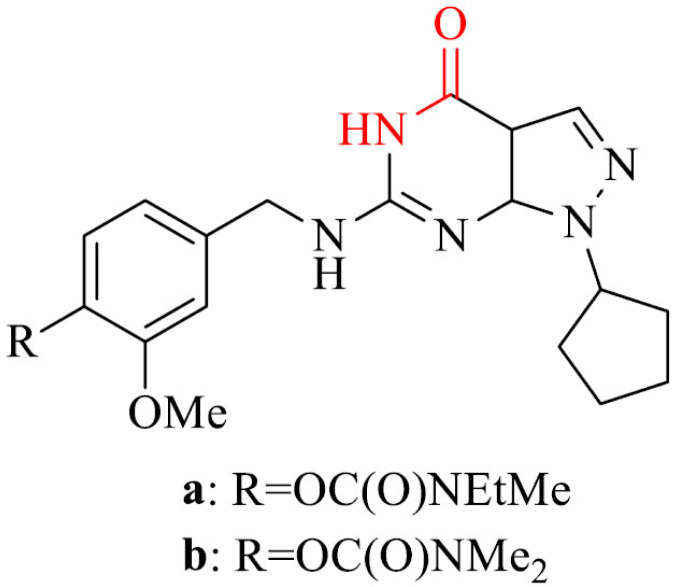
|
Inhibition of PDE9A | [153] |
| 27 |
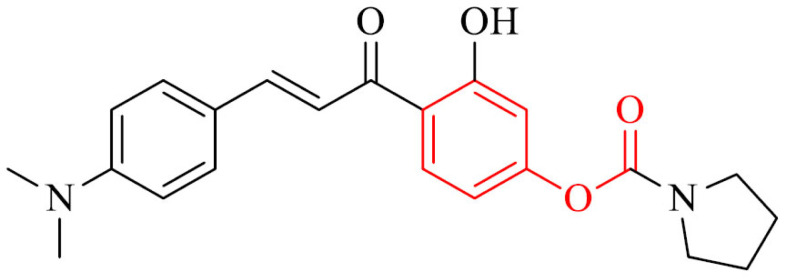
|
Ability to inhibit self-induced and Cu2+-induced Aβ1-42 aggregation, inhibitory activity against MAO-B, antioxidative properties, ability to chelate metals and to cross the BBB in vitro | [154] |
| 28 |
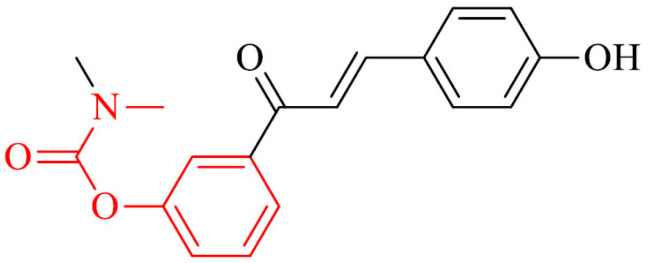
|
Prevention from ROS in SH-SY5Y cell line | [155] |
| 29 |
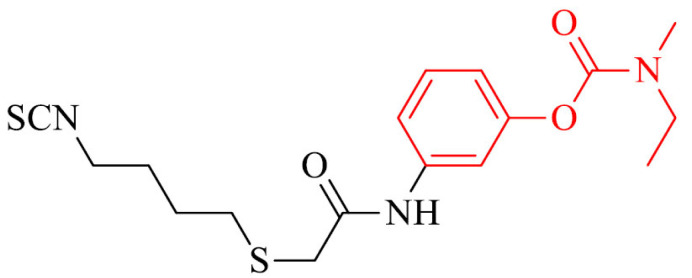
|
Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activity in BV-2 cells, the induction of proteins expression (i.e. GSH) involved in the antioxidant defense in SH-SY5Y cell line, a decrease of ROS levels and NO-release in BV-2 cells | [156] |
| 30 |
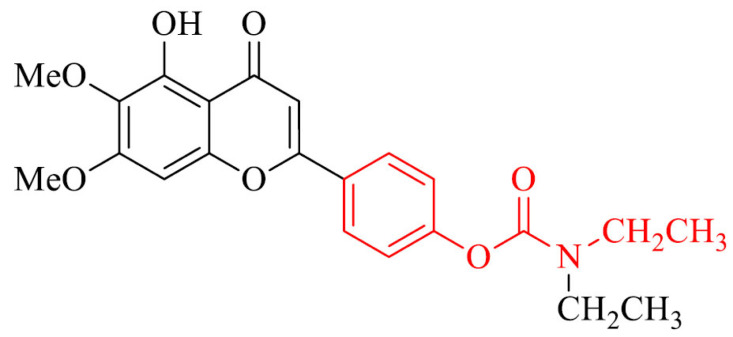
|
Antioxidative activity, selective metal chelator and neuroprotector against H2O2-induced PC12 cell injury, ability to pass the BBB in vitro, relevant neuroprotective effects in scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment in mice model | [157] |
| 31 |
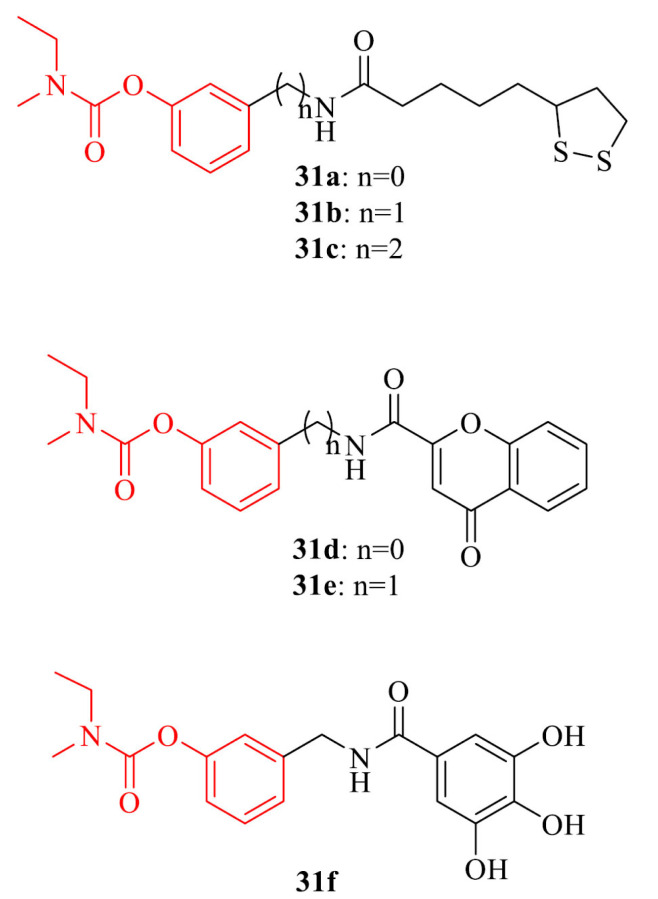
|
31a-c: pleiotropic activities 31d-f: protection from the self-mediated Aβ aggregation, 31e,f: neuroprotective effect in HT22 cells against glutamate-índuced neuronal death |
[158] |
| 32 |
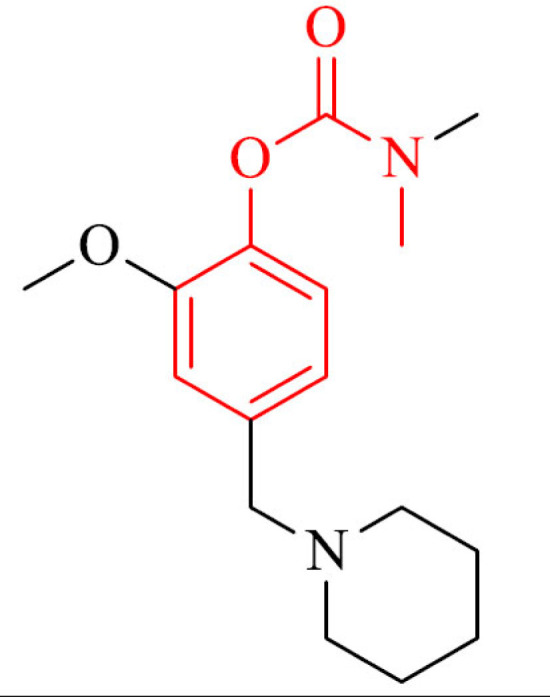
|
Prevention of Aβ self-aggregation in TEM observation, ABTS+ scavenging, and ability to chelat Cu2+ ions | [159] |
| 33 |
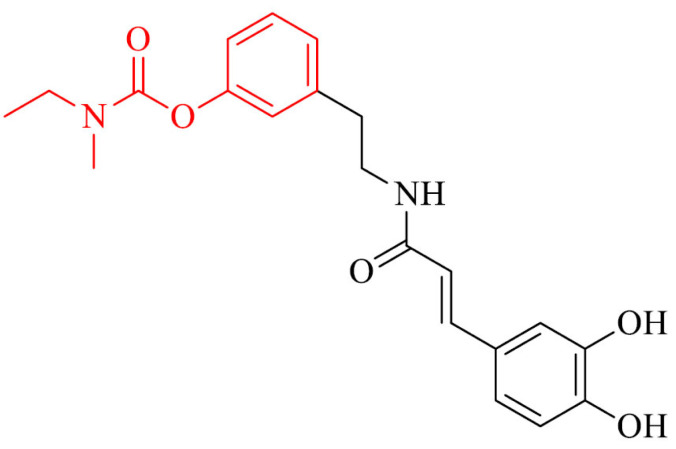
|
Prevention of Aβ self-aggregation, protection of HT22 cells from glutamate and H2O2 induced cell death, scavenging free radicals and Cu2 ions chelation | [160] |
| 34 |
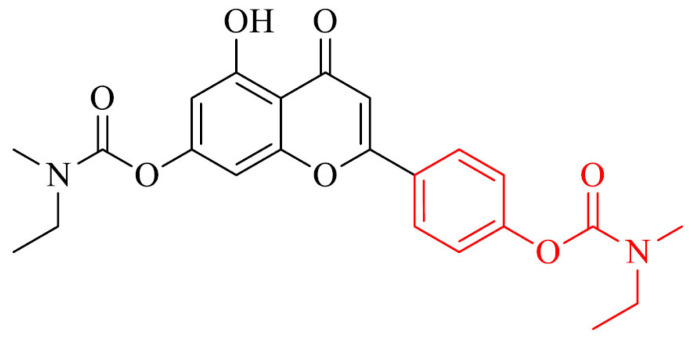
|
Antioxidant activity, neuroprotection of H2O2- induced PC12 cells and Aβ1-42- induced SH-SY5Y cells, hepatoprotection of H2O2- induced LO2 cells, selective metal chelator, activity against Cu2+/hAChE/self-induced Aβ1-42 aggregation, disaggregation of Cu2+-induced Aβ1-42 aggregation, ability to pass the BBB in vitro | [161] |
