Fig. 3. Functional studies of the interacting residues in β1-AR for the activation of Gi.
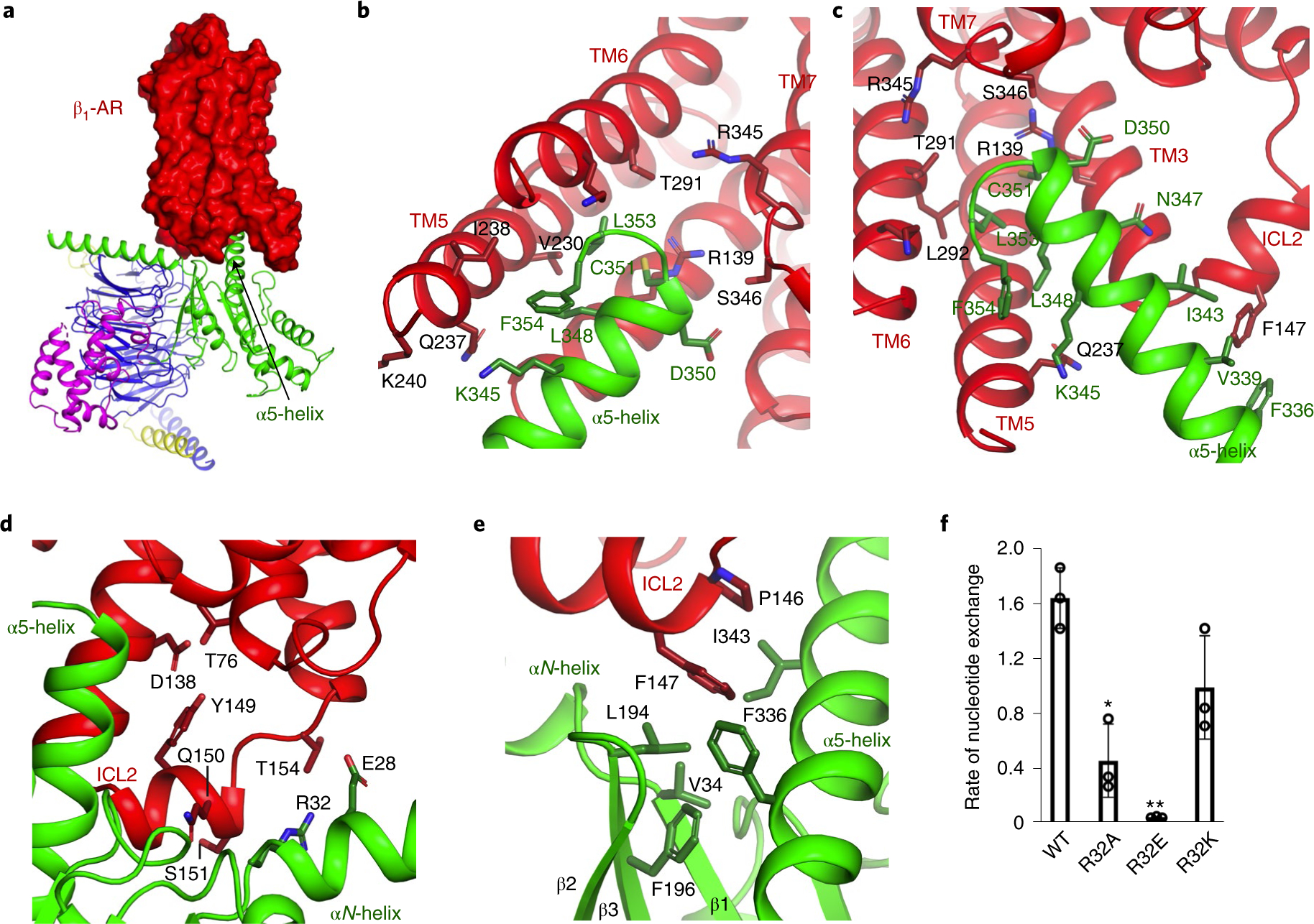
a, β1-AR uses its cytoplasmic surface like a saddle to cradle the α5-helix of the Ras-like domain of Gαi. b,c, Interactions between β1-AR and the α5-helix of Gα as viewed from different angles. d–f, Role of the interaction between ICL2 of β1-AR and the N-terminal hinge between the αN-helix and β1-strand of Gαi in Gi activation by β1-AR. ICL2 of β1-AR (in red) interacts with the N-terminal hinge between the αN-helix and β1-strand of Gαi (in green) as well as the α5-helix and the β2-β3 loop of Gαi (d,e). Activation of wild-type and mutant Gαi proteins by β1-AR monitored by the BODIPY-GTPγS binding (f). Data from three independent experiments of the BODIPY-GTPγS binding assays are shown, and the initial rate of BODIPY-GTPγS binding catalyzed by β1-AR is reported as mean±s.d. *P =0.004; **P= 0.0002 (Student’s t-test).
