Fig. 4. Comparative structural analysis of the complexes of isoproterenol–β1-AR–Gi and isoproterenol–β1-AR–Gs.
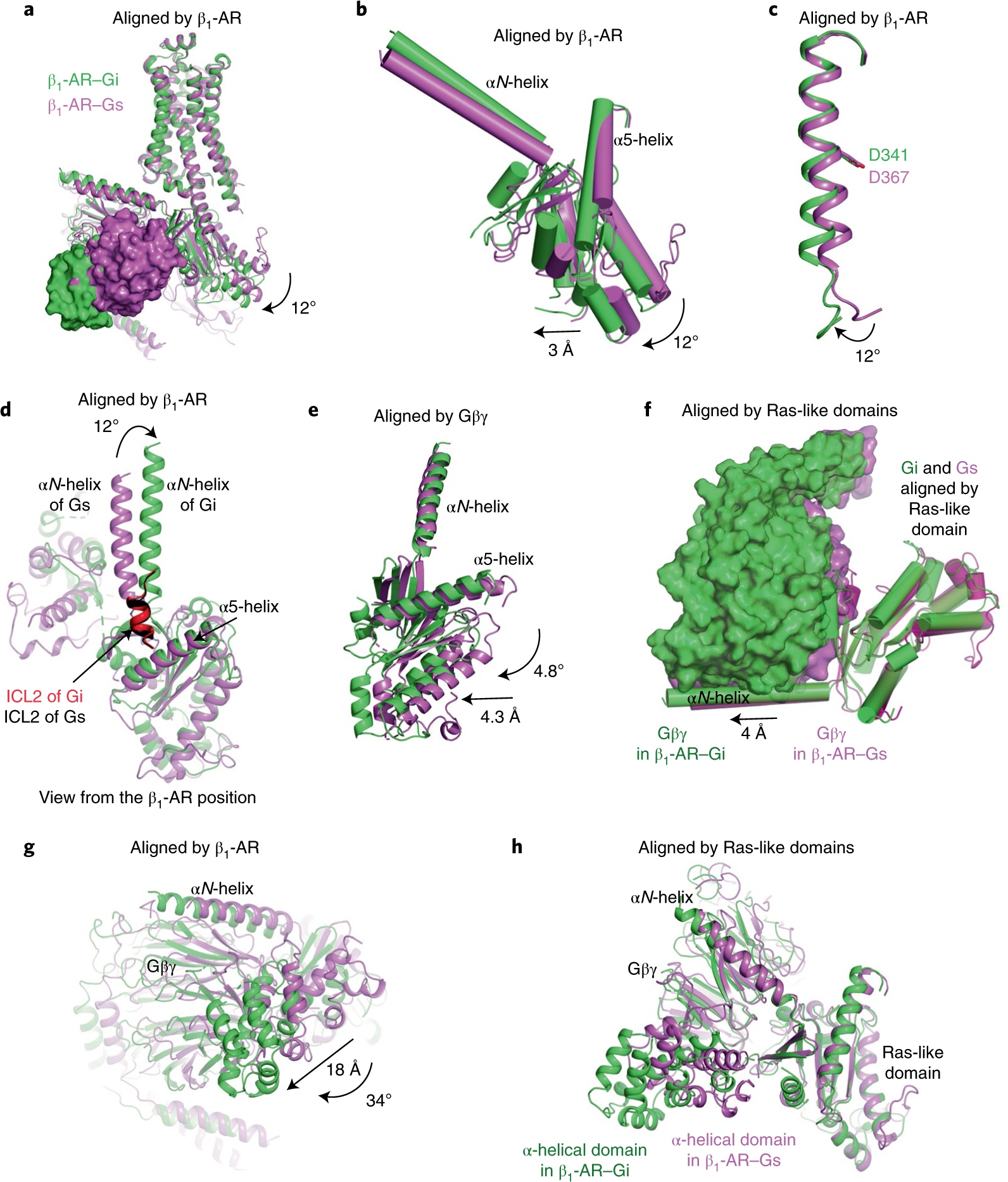
a–e, Comparisons of the β1-AR–Gi complex (green) and the β1-AR–Gs complex (violet), aligned by the β1-ARs (a), the Ras-like domains in the β1-AR–Gi complex (green) and the β1-AR–Gs complex (violet), aligned by the β1-ARs (b), the α5-helices in the β1-AR–Gi complex (green) and the β1-AR–Gs complex (violet), aligned by the β1-ARs (c), the αN-helices in the β1-AR–Gi complex (green) and the β1-AR–Gs complex (violet), aligned by the β1-ARs (d) and the Ras-like domains in the β1-AR–Gi complex (green) and the β1-AR–Gs complex (violet), aligned by the Gβγ subunits (e). f, Comparison of the distance between the Ras-like domain and Gβγ in the β1-AR–Gi complex (green) and the β1-AR–Gs complex (violet), aligned by the Ras-like domains. g, Relative locations of the α-helical domains in the β1-AR–Gi complex (green) and the β1-AR–Gs complex (violet) when the receptors are superimposed. h, Relative locations of the α-helical domains in the β1-AR–Gi complex (green) and in the β1-AR–Gs complex (violet) when the Ras-like domains are superimposed.
