Figure 7: CXCR6 expression predicts survival in human cancer patients.
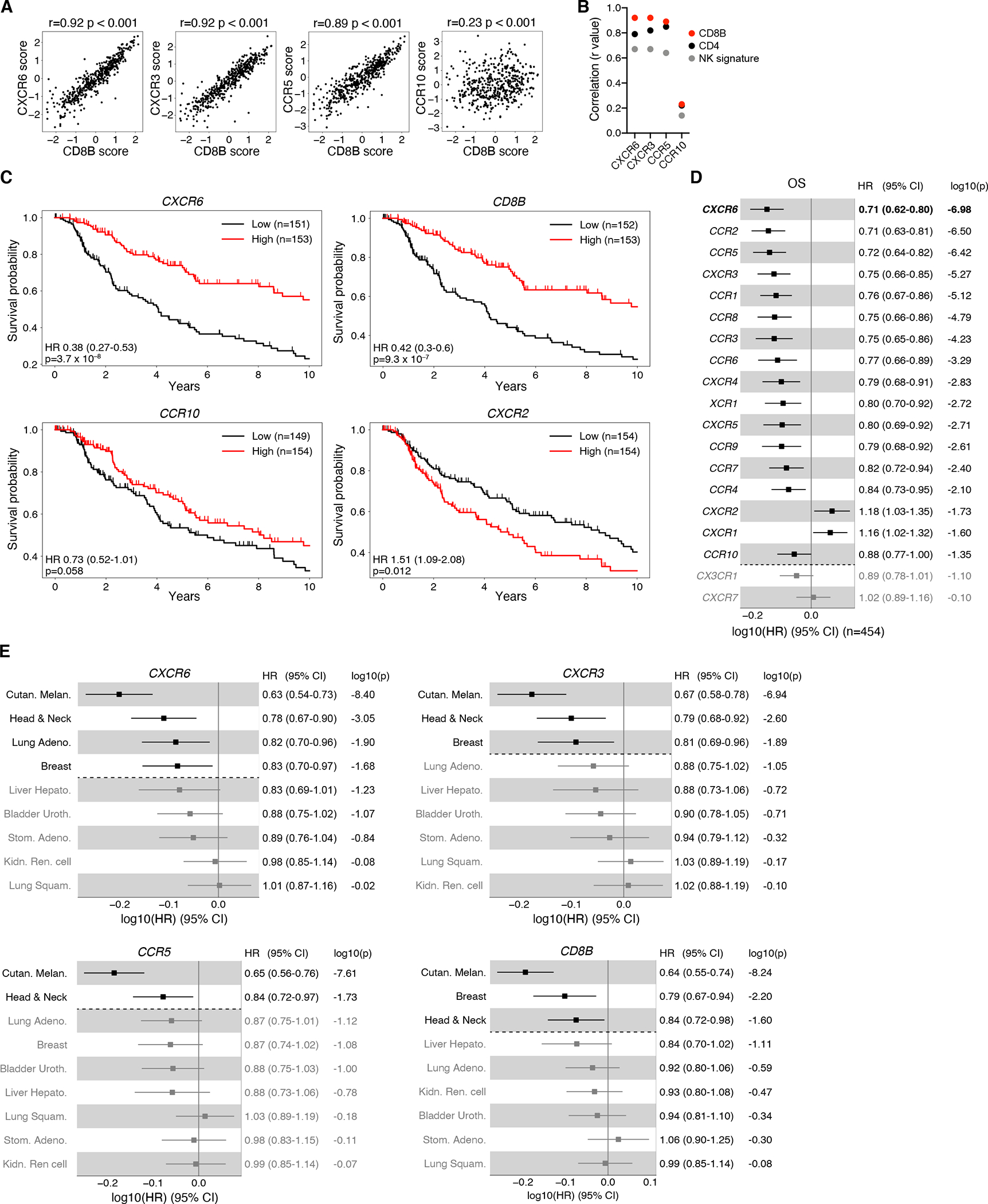
(A) Correlation between chemokine receptor and CD8B expression scores in tumor tissue of 469 TCGA melanoma (SKCM) patients. Spearman’s rank-correlation coefficient r and two-sided P value are shown.
(B) Summary of rank-correlation coefficients between indicated chemokine receptors and CD8B, CD4, or NK signature (NCR1 and SH2D1B) expression scores.
(C) Kaplan-Meier estimates of overall survival comparing the top (“High”) and bottom (“Low”) third of melanoma patients with regard to expression scores of indicated genes. Hazard ratios (HR), 95% confidence intervals (CI), and P values (Wald Chi-Squared test) based on univariate Cox proportional-hazards model (High versus Low). Tick marks indicate censoring.
(D) Association between overall survival and continuous expression score of individual chemokine receptor genes in melanoma patients. HR, 95% CI, and P values (Wald Chi-Squared test) based on univariate Cox proportional-hazards model. Note: a HR of e.g. 0.71 (CXCR6) indicates that at any time during the TCGA melanoma study period patients had a 1–0.71 = 0.29 = 29% reduction in risk of death per one standard deviation increase of normalized log2 transformed CXCR6 expression + pseudo count.
(E) Association between overall survival and continuous expression score of indicated genes in all indicated cancer types, adjusted for Sex (versus Male) and AJCC pathologic tumor stage (versus Stage 0 & I).
Significant (P < 0.05) associations shown in black in (D, E).
