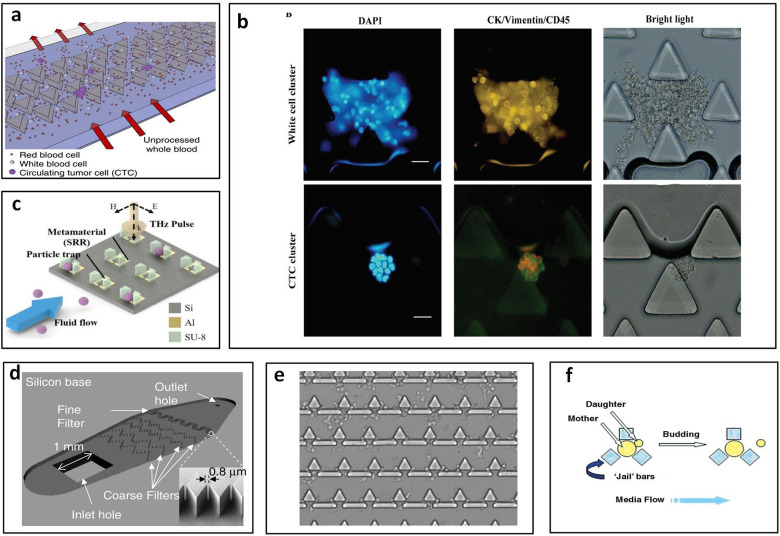
FIG. 4.
Polygonal micropost cell trapping arrays. (a) Schematic of triangular microposts in which CTC clusters are captured from unprocessed whole blood while single cells pass through. Reproduced with permission from Sarioglu et al., Nat. Methods 12, 685–691 (2015). Copyright 2015 Springer Nature. (b) Representative fluorescent images of white cell cluster (upper) and CTC cluster (lower) trapped in triangular pillar array. Scale bars, 20 μm. Reproduced with permission from Gao et al., Oncotarget 8, 12917–12928 (2016). Copyright 2016 Authors, licensed under a CC BY 3.0. (c) Schematic of the proposed microfluidic metamaterial sensor (MMS) operating in the THz spectral region. Reproduced with permission from Shih et al., J. Appl. Phys. 121, 023102 (2017). Copyright 2017 AIP Publishing LLC. (d) Schematic of the filter-based microfluidic device with SEM image showing the diamond-shaped pillars. Reproduced with permission from Zhu et al., Biomed. Microdevices 9, 745–750 (2007). Copyright 2007 Springer Nature. (e) White blood cells trapped after whole blood is flowed into the sample inlet. Reproduced with permission from Kuan et al., Sci. Rep. 8, 15345 (2018). Copyright 2018 Authors, licensed under a CC BY 4.0. (f) “Jail” traps for yeast during typical asymmetric budding; daughter cells are then washed away with media flow. Reproduced with permission from Ryley and Pereira-Smith, Yeast 23, 1065–1073 (2006). Copyright 2006 John Wiley and Sons.