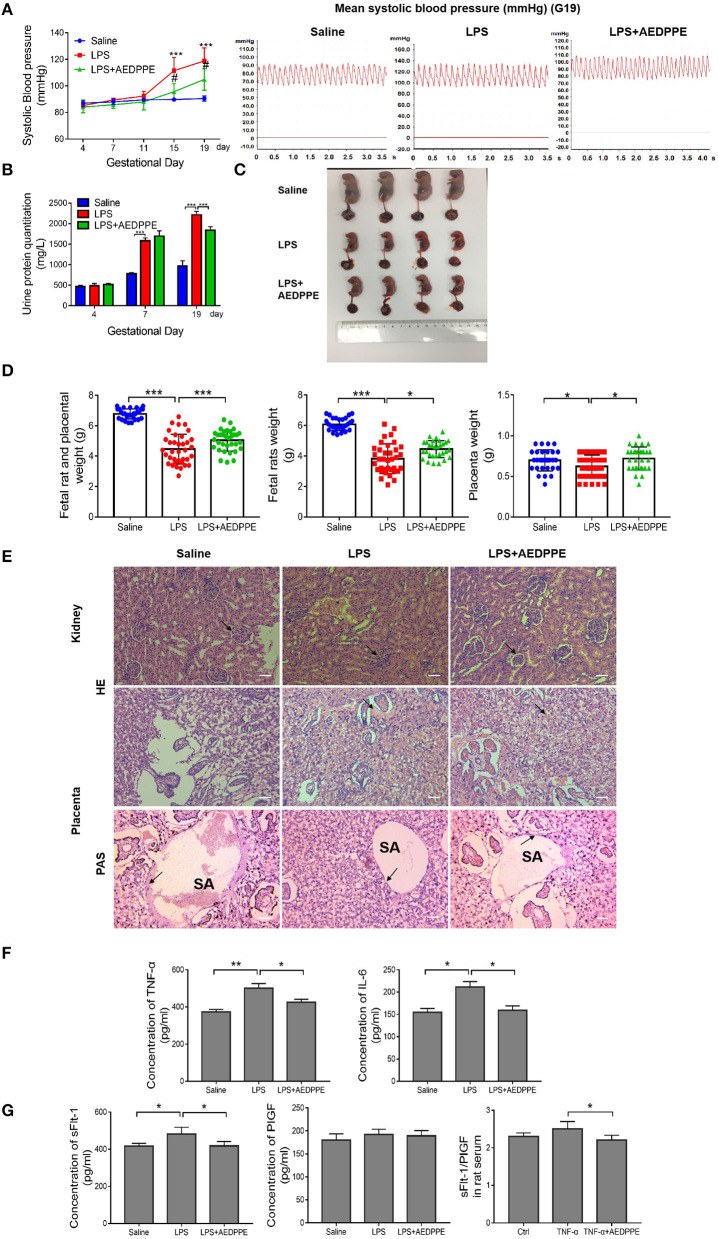
Figure 5.
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) injection causes a variety of symptoms similar to PE, including increased urinary protein, elevated blood pressure, kidney, and placental damage, and very pronounced fetal growth restriction in fetal rats. These symptoms were significantly improved in the LPS+AEDPPE group. (A) Blood pressure in rats of the physiological saline group (n = 6), LPS group (n = 6), and LPS+AEDPPE group (n = 6). (B) Urine protein levels on day 4, day 7 and day 19 of pregnancy of each group. (C) Fetal rats in the LPS group exhibited significant growth restriction compared to those in the saline group. AEDPPE exerted a protective effect against fetal growth restriction. (D) Weight of fetal rats and placenta in each group. (E) The glomeruli in the LPS group showed mild chronic hyperplasia and swelling compared to the glomeruli of the saline group. Compared to the saline group, H&E staining showed significant vascular congestion in the placental labyrinth, which was improved in the LPS+AEDPPE group. PAS staining in the saline group showed significant fibrin deposition; in contrast, in the LPS-treated group there was little fibrin deposition; and in the LPS+AEDPPE group, a small amount of fibrin could be observed. SA, spiral artery (bar [H&E] = 200 μm, Bar [PAS] = 400 μm). (F) Compared with the control group, the serum concentrations of TNF-α (p < 0.01) and IL-6 (p < 0.05) were significantly higher in the LPS rats; and the concentrations of TNF-α (p < 0.05) and IL-6 (p < 0.05) were significantly lower in the LPS+AEDPPE group compared with the LPS group. (G) The concentrations of sFlt-1 and PlGF in the serum of each group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. H&E, hematoxylin–eosin; IL, interleukin; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; PAS, periodic acid-Schiff; PlGF, placental growth factor; sFlt-1, soluble FMS-like tyrosine kinase 1; TNF-α, tumor-necrosis factor alpha.