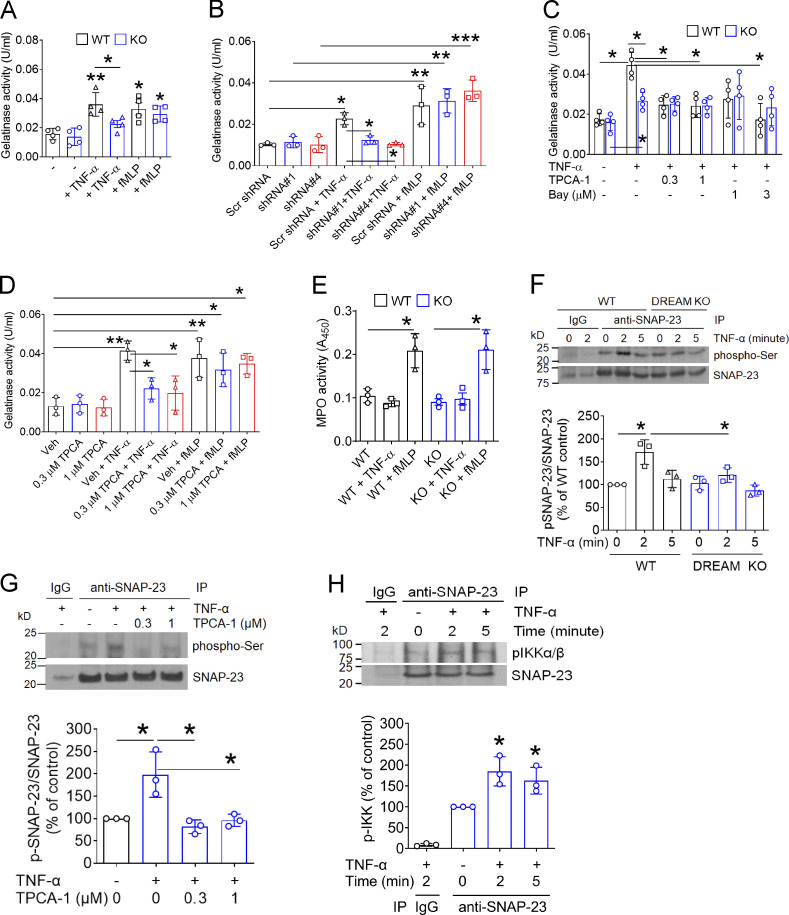
Figure 5.
Neutrophil DREAM promotes degranulation through IKKβ-mediated SNAP-23 phosphorylation. (A and C) WT and DREAM KO neutrophils were treated without (A) or with (C) vehicle (−, 0.1% DMSO) or a different concentration of TPCA-1 and Bay 11–7082. Cells were then incubated with 5 ng/ml TNF-α or 10 µM fMLP for 10 min. The releasate was used to measure gelatinase activity (n = 3). (B) dHL-60 cells pretreated with control or DREAM shRNA were incubated with TNF-α or fMLP. The supernatant was collected and used in the gelatinase activity assay. (D) Human neutrophils were pretreated with 0.3–1 µM TPCA-1 and then incubated with or without TNF-α or fMLP. The supernatant was collected and used in the gelatinase activity assay. (E) WT and DREAM KO neutrophils were treated with or without TNF-α or fMLP and used for an MPO activity assay with the supernatant. (F) WT or DREAM KO neutrophils were treated with or without TNF-α for 0–5 min. (G) WT neutrophils were pretreated with 0.1% DMSO (−) or 0.3–1 µM TPCA-1 and then treated with or without TNF-α for 5 min. (H) WT neutrophils were treated with or without TNF-α for 2 or 5 min. The lysates were immunoprecipitated with control IgG or anti–SNAP-23 antibodies and subjected to immunoblotting with anti–phospho-Ser, anti–SNAP-23, or anti-pIKKα/β antibodies and densitometric analysis. Data represent the mean ± SD (n = 3 or 4). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 versus unstimulated neutrophils or two groups after Student’s t test (A and E) or after ANOVA and either Tukey’s test (B–D, F, and G) or Dunnett’s test (H). Bay, Bay 11–7082; IP, immunoprecipitation; Scr, scrambled; Veh, vehicle.