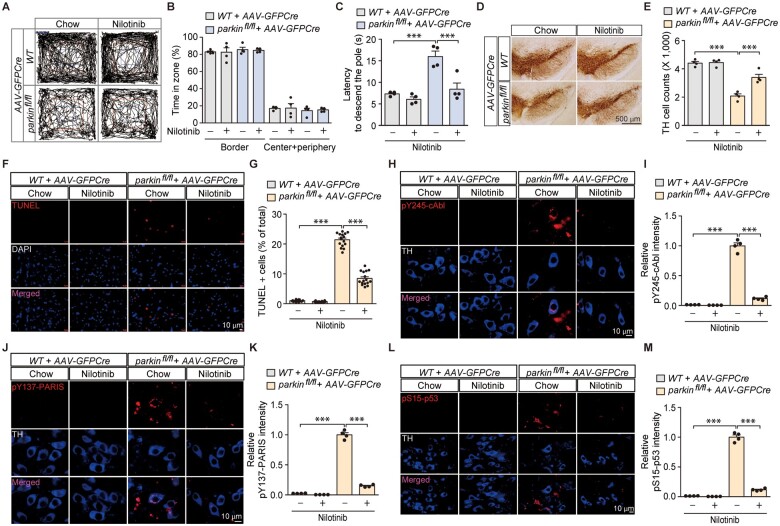
Figure 6.
Pharmacological inhibition of c-Abl activity in in vivo adult parkin knockout mice prevents motor dysfunction and dopaminergic neurodegeneration with concomitant blocking of PARIS phosphorylation and p53 activation. (A) Representative exploratory paths from an open-field test of 6-month-old wild-type littermate or homozygous floxed parkin mice (parkinfl/fl) nigrally injected with AAV-GFPCre (3 m) and treated with the c-Abl inhibitor nilotinib (200 mg nilotinib per 1 kg diet, p.o. for 2 months) or standard chow diet (chow). (B) Anxiety assessment of each experimental mouse group examining the percentage of exploration time in the border versus the sum of the centre and periphery zones (n = 4 mice per group). (C) Pole test for motor function assessment of each experimental mouse group used in B examining the latency to reach the base of the vertical pole (n = 4 mice per group). (D) Representative TH immunohistochemical staining of substantia nigra from wild-type or homozygous floxed parkin mice (parkinfl/fl) with intranigral injection of AAV-GFPCre with or without nilotinib treatment (200 mg nilotinib per 1 kg diet, p.o. for 2 months). Scale bar = 500 µm. (E) Stereological assessment of TH-positive dopaminergic neurons in the SNpc (injection side) of the indicated mouse groups (n = 4 mice per group). (F) Representative TUNEL assay images of ventral midbrain from wild-type littermate or homozygous floxed parkin mice (parkinfl/fl) that experienced stereotaxic nigral injection of AAV-GFPCre with or without nilotinib treatment (200 mg nilotinib per 1 kg diet, p.o. for 2 months). The coronal brain sections were counterstained with DAPI. Magnified images are shown in the bottom panel. (G) Quantification of the percentage of TUNEL-labelled cells in AAV-GFPCre-injected ventral midbrain regions from wild-type littermate and parkinfl/fl mice with or without nilotinib treatment (n = 16 sections from four mice per group). (H) Representative immunofluorescence images examining the expression of pY245-c-Abl in TH-stained dopamine neurons from the AAV-GFPCre-injected ventral midbrain regions of wild-type littermate and parkinfl/fl mice with or without nilotinib treatment. (I) Quantification of the relative pY245-c-Abl fluorescence signal in the ventral midbrain regions of the indicated experimental groups (n = 4 mice per group). (J) Representative immunofluorescence images examining the expression of pY137-PARIS in TH-stained dopamine neurons from the AAV-GFPCre-injected ventral midbrain regions of wild-type littermate and parkinfl/fl mice with or without nilotinib treatment. (K) Quantification of the relative pY137-PARIS fluorescence signal in the ventral midbrain regions of the indicated experimental groups (n = 4 mice per group). (L) Representative immunofluorescence images examining the expression of pS15-p53 in TH-stained dopamine neurons from the AAV-GFPCre-injected ventral midbrain regions of wild-type littermate and parkinfl/fl mice with or without nilotinib treatment. (M) Quantification of the relative pS15-p53 fluorescence signal in the ventral midbrain regions of the indicated experimental groups (n = 4 mice per group). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using an ANOVA test followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis or an unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. ***P < 0.001. WT = wild-type.