FIGURE 5.
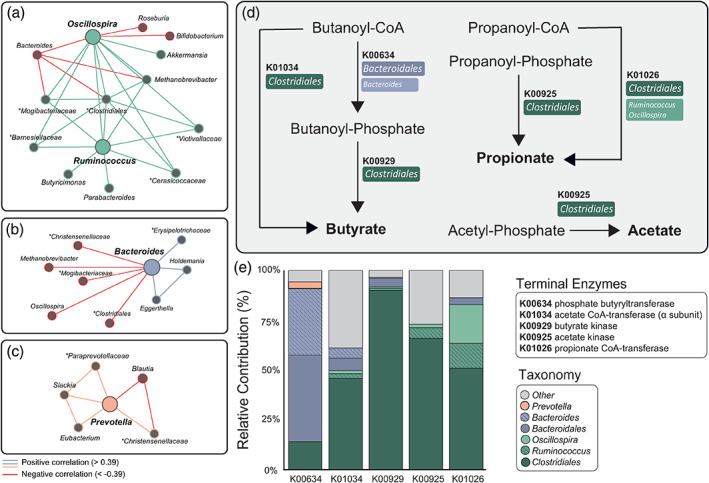
Link between microbiota genera associated to threat‐related brain processes and functional pathways supporting the production of short‐chain fatty acids. Co‐occurrence and co‐exclusion relationships between the driving genera (large nodes) including (a) Ruminococcus/Oscillospira, (b) Bacteroides, and (c) Prevotella. Unclassified genera are described at a broader taxonomic rank above genus level (i.e. family or order) and are marked by asterisks. Graphs are visualised as a force‐directed layout using Gephi (Version 0.9.2), using the force atlas template (Bastian et al., 2009). (d) Metabolic pathways (derived from the Kyoto Encyclopaedia of Genes and Genomes pathways) representing final enzymatic conversions (terminal enzymes) involved in butyrate, propionate, and acetate production. The major contributor(s) to each gene‐encoding enzyme have been identified in coloured boxes. (e) Decomposition of core/major genera and orders contributing to SCFA pathways. Dark tones represent contributions from a higher taxonomic rank: order. Hatched and lighter tones represent contributions from driving genera
