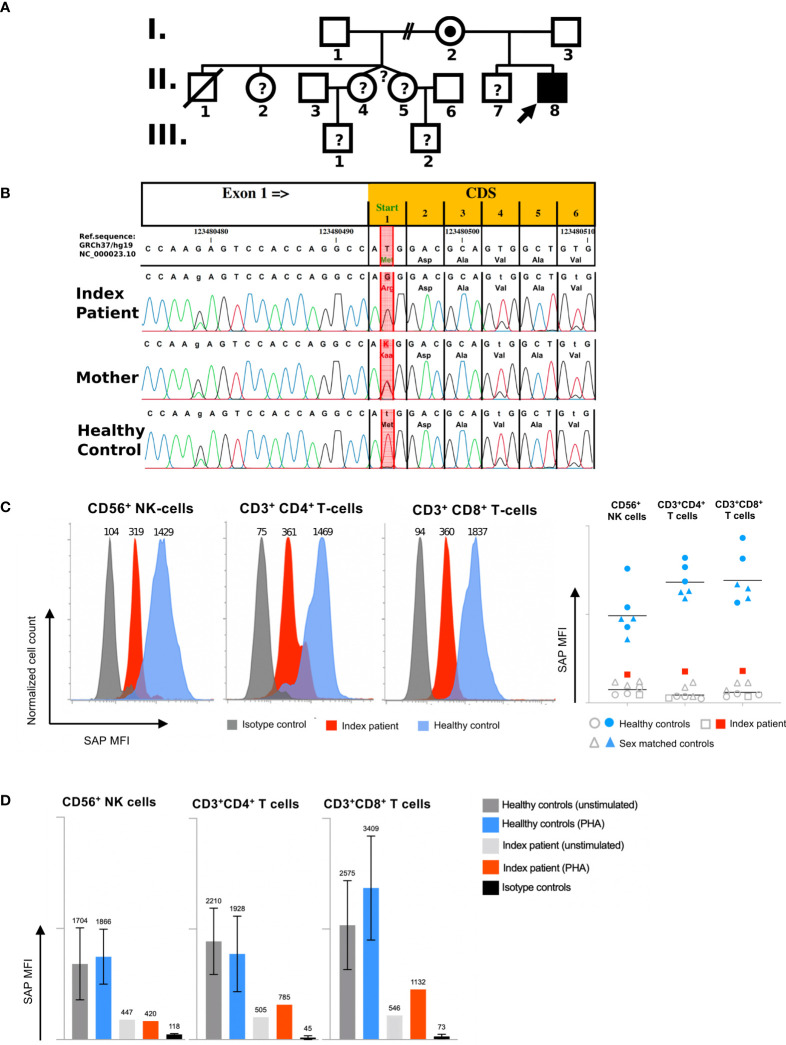
Figure 3.
Molecular and functional characterization of a novel SH2D1A mutation: (A) Family Pedigree. The arrow indicates the index patient. Mutation analysis confirmed a hemizygous SH2D1A mutation in patient II,8 and female carrier status in his mother I,2. One half-brother died at the age of 3 from acute leukaemia after suspected EBV infection (II,1), without confirmation of the XLP1 genotype by sequencing. No genetic analysis could be performed in other family members (indicated by question marks). (B) Results of Sanger sequencing of SH2D1A of the index patient, the mother and a healthy male individual are shown. Red column indicates position of the start codon mutation (ChrX:g.123480494 T>G; GRCh37/hg19). (C) Intracellular SAP expression due to novel SH2D1A mutation. Mean fluorescence intensities (MFI) representing intracellular SAP expression in CD56+ NK-cells, CD4+ T-cells, and CD8+ T-cells of one representative healthy control (blue), and the index patient (red) are shown in histograms (isotype control staining is shown in grey). Diagram of MFI representing SAP expressions of six healthy controls consisting of 3 male sex matched controls (shown as blue triangles) and 3 anonymous blood donors (shown as blue dots), the index patient (shown as red squares) and relating isotype control staining (shown as grey rings, triangles and squares) are shown in the right figure (lines represent geometric mean). (D) Quantification analysis of intracellular SH2D1A expression. MFI of intracellular SH2D1A expression in CD56+ NK-cells, CD3+CD4+ T-cells and CD3+CD8+ T-cells from five healthy controls including 3 male sex matched controls and 2 anonymous blood donors as well as the SH2D1A-deficient index patient following 3 days of PHA (phytohemagglutinin)-stimulation are shown (bars and top numbers represent mean values, error indicators represent standard deviations, staining of isotype controls are shown in black).