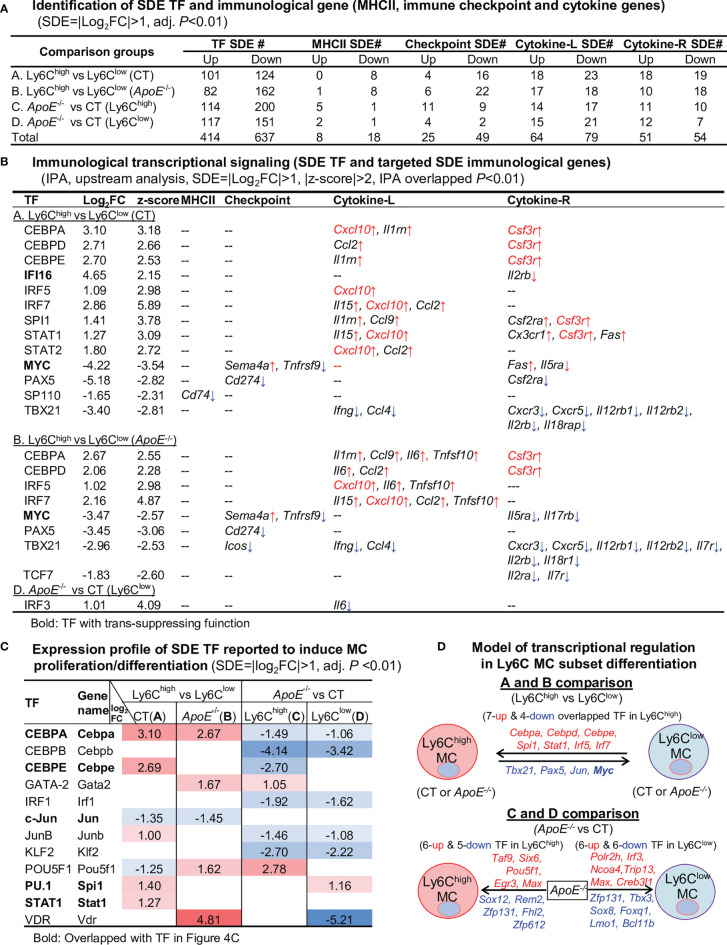
Figure 4.
Identification of SDE TF, immunological gene and transcriptional regulatory models. (A) Identification of SDE TF and immunological genes. SDE TF (1150) and MHCII (28), immune checkpoint (82), cytokine ligand (135) and receptor (89) were identified using the criteria of |Log2FC|>1 (2-FC) and adjusted P<0.01. (B) Immunological transcriptional signaling. SDE immunological genes were matched with SDE TF by IPA upstream analysis. Transcriptional regulatory relationship between SDE TF and SDE immunological genes was justified by p-value<0.01 and |z-score|>2. The detailed list of SDE TF matching with the corresponding SDE gene is presented in Supplementary Table 2 . ↑, upregulated; ↓, downregulated (C) Expression profile of SDE TF reported to induce MC proliferation/differentiation. Twelve SDE TF involved in MC generation are differentially expressed in four comparison groups in these subsets. Numbers with red-colored background indicate fold change>2 (log2FC>1). Numbers with blue-colored background indicate fold change<0.5 (log2FC<-1). The completed list of TF reported to induce MC proliferation/differentiation is in Supplementary Table 3 . (D) Model of transcriptional regulation in Ly6C MC subset differentiation. Model describes potential transcriptional regulatory machinery. In A and B comparison, we identified 7-upregulated and 5-downregulated overlapped TF regulating Ly6C MC differentiation. In comparison C, 11 SDE TF (6 up and 5 down) are identified in ApoE-/- Ly6Chigh MC. While, in comparison D, 12 SDE TF (6 up and 6 down) are identified in ApoE-/- Ly6Clow MC. Red letter highlighted the representative up-regulated gene. Blue letter highlighted down-regulated genes.