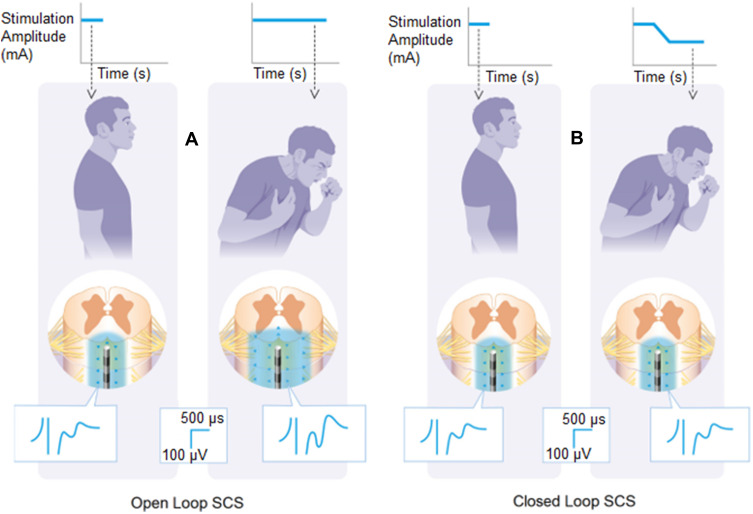
Figure 3.
When the patient coughs, the spinal cord stimulation leads move closer to the spinal cord. This is detected by the spinal sensors as an increase in evoked compound action potential (ECAP) amplitude. In the open-loop configuration (A), the stimulation parameters are fixed; as such, the ECAP and volume of tissue activated (VTA, the blue area surrounding the electrodes) grows with the electrode-cord spacing decrease. In the closed-loop configuration (B), the system senses the increasing ECAP and automatically decreases the stimulation amplitude to maintain a constant VTA and ECAP amplitude.