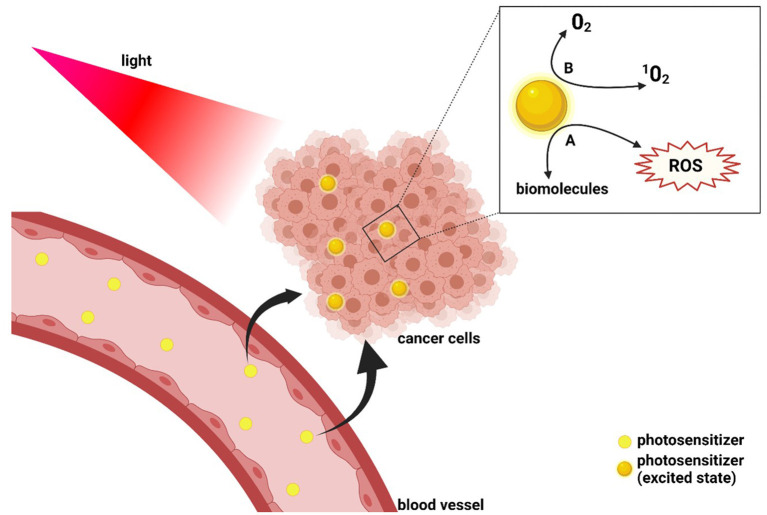
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of photodynamic therapy mechanism of function. After administration, the photosensitive agent is irradiated at a wavelength that matches its absorption properties. The excitation of the photosensitiser leads to two different types of reaction: the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) as a result of the interaction of the photosensitiser with biomolecules (Reaction A) and the generation of singlet oxygen (Reaction B).