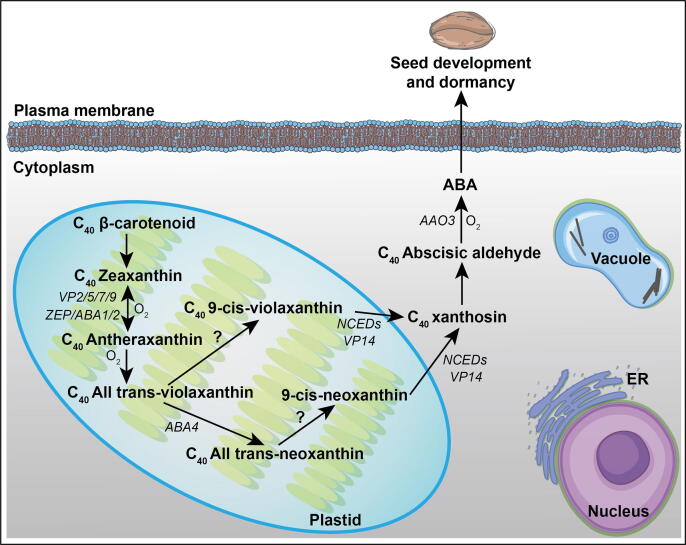
Fig. 1.
Regulation of seed development and dormancy by ABA biosynthesis through the carotenoid pathway started from β-carotene (C40). The complete ABA synthesis process takess place in plastids and cytoplasm where ZEAXANTHIN EPOXIDASE (VPs, ZEP, ABA1/2) converts zeaxanthin into antheraxanthin and all trans-violaxanthin. ABA4 catalyzes the conversion from all-trans-violoxanthin to the all-trans-neoxanthin. The conversion of xanthoxin from 9′-cis-neoxanthin and 9′-cis-violaxanthin is exerted by VP14 and NCEDs (NINE-CIS-EPOXYCAROTENOID DIOXYGENASE), among which the NCEDs display different subcellular localization of plastid or cytoplasm. The oxidation of abscisic aldehyde by AAO3 (ABSCISIC ALDEHYDE OXIDASE3) is responsible for the conversion from abscisic aldehyde into ABA, which in turn induces and maintains seed dormancy. But, it is yet unknown of the factors responsible for the conversion from all-trans-violoxanthin /all-trans-neoxanthin to 9-cis-violoxanthin/9-cis-neoxanthin.