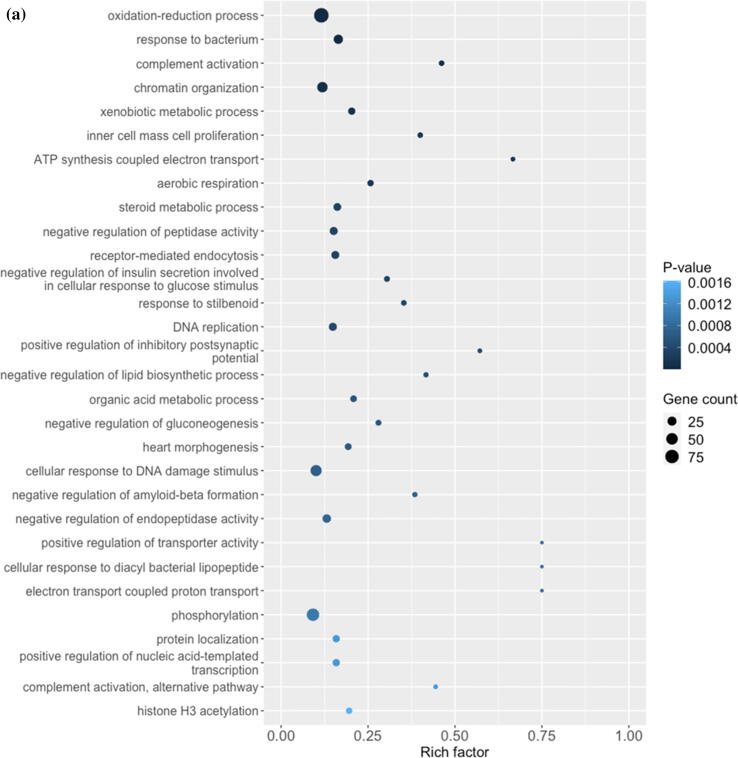
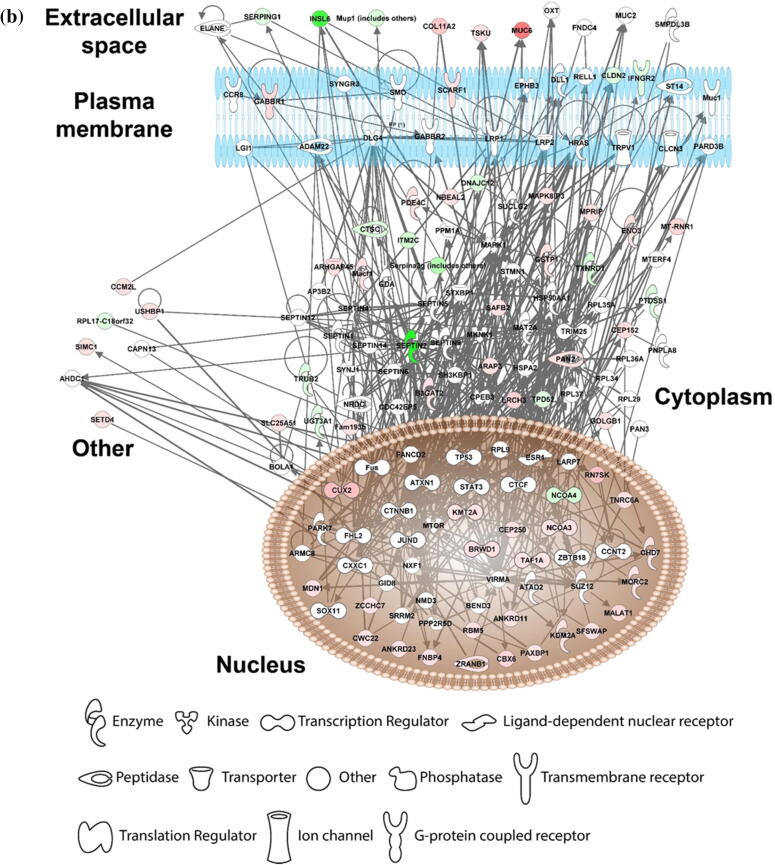
Fig. 2.
Diagrams showing vitamin C relieves FOA-induced hepatotoxicity by controlling gene expression. The comparative transcriptomic analysis reveals differential gene expression induced by vitamin C (PFOA vs vitamin C + PFOA group). (a) The DEGs were assessed by the Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis. The rich factor plot shows that the vitamin C-relieved PFOA-altered biological processes (p < 0.05). (b) Data from gene network analysis using IPA, demonstrating cell signaling involved in the protective action of vitamin C.