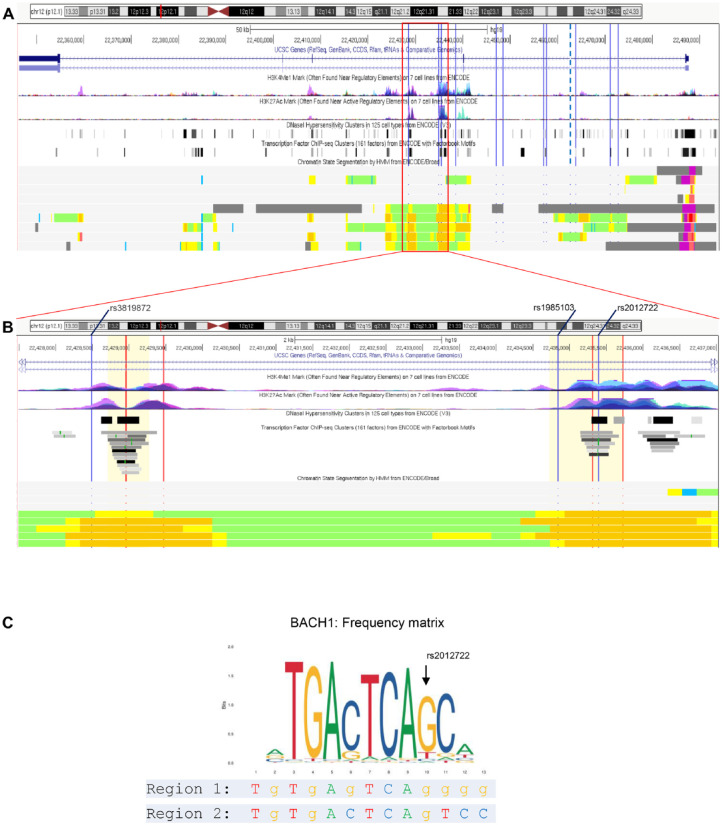
Figure 2.
Genome-wide association study (GWAS)–nominated linkage disequilibrium (LD)–single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and 2 putative regulatory regions at ST8SIA1. (A) The sentinel SNP (lead SNP) rs2728821 is marked with a bold dotted vertical line and the 11 LD-SNPs are marked with thin lines. From top: The first panel shows the chromosomal hg19 positions and the exon-intron structure of ST8SIA1. This gene is transcribed in reverse orientation with the promoter on the right. The second panel shows the ENCODE-derived H3K4me1 and H3K27ac methylation marks from 7 cell lines that are often associated with the higher activation of transcription and are defined as active enhancer marks. The third panel presents the ENCODE-derived DNase I hypersensitive sites from 125 cell types. These accessible chromatin zones are functionally related to transcriptional activity. The fourth panel presents the binding regions that were determined for 161 TFs by chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq) experiments of ENCODE. This panel does not show the exact transcription factor binding site (TFBS) but indicates transcription factor (TF) binding was found at these chromatin regions. The bottom panel displays chromatin state segmentation for several human cell types (GM12878, H1-hESC, K562, HepG2, HUVEC, HMEC, HSMM, NHEK, NHLF) using a hidden Markov model (HMM) with ChIP-seq data for 9 TFs functionally related to transcriptional activity as input. The states are colored to highlight predicted functional elements (orange = strong enhancer, yellow = weak enhancer, green = weak transcribed, blue = insulator, red = active promoter, purple = poised promoter). (B) Closeup view of panel A. At 2 chromatin regions, several LD-SNPs locate within strong enhancers predicted by HMM chromatin state segmentation patterns. The chromosomal hg19 positions are given in the top panel. The 3 LD-SNPs are marked with blue lines. The regions covered by the reporter gene constructs are highlighted with lemon chiffon color. The positions of the single-guide RNAs (sgRNAs) are marked in red. (C) Frequency matrix (from Jaspar). The common G allele of SNP rs2012722 is predicted to be required for BACH1 binding, whereas the rare T allele strongly reduces binding affinity. Under the matrix, the DNA sequences of Region 1 (regulatory element tagged by rs3819872) and Region 2 (regulatory element tagged by rs2012722) at the predicted BACH1 binding motif are indicated.