Figure 4.
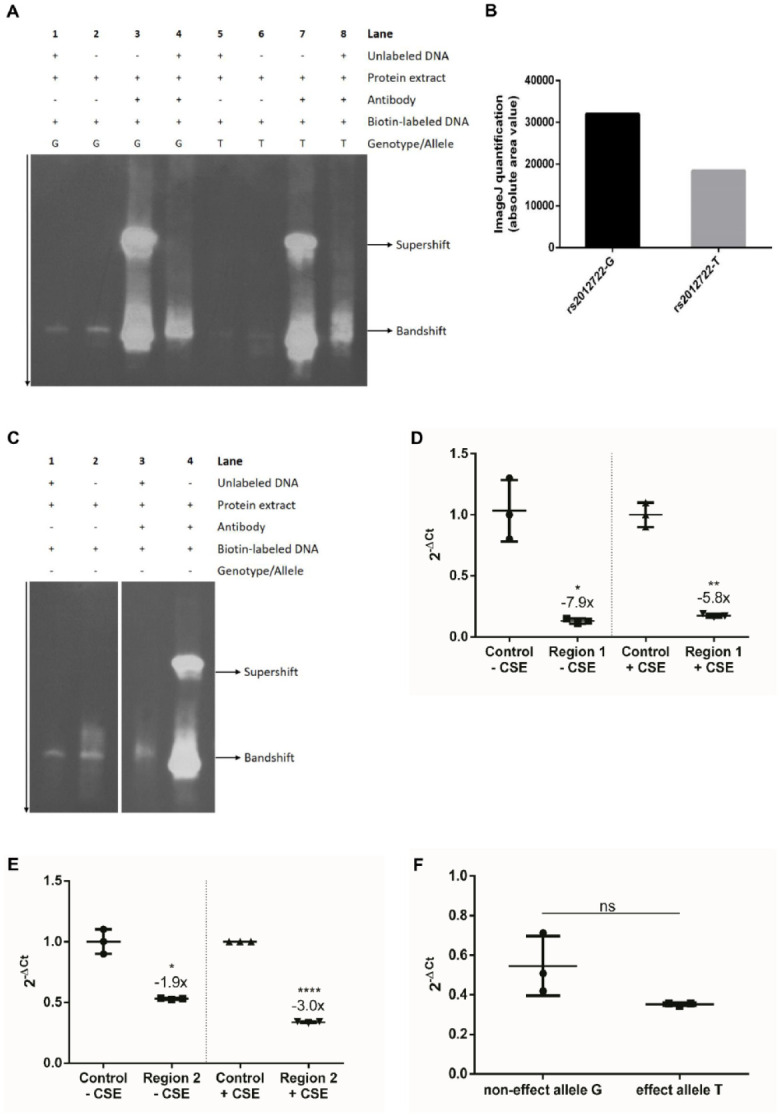
The disease-associated regulatory elements at ST8SIA1 show repressor activity and BACH1 binding. (A) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) indicated BACH1 binding at rs2012722 and revealed allele-specific effects on the binding affinity. Lanes 1 to 2 and 5 to 6 show EMSA without BACH1 antibody. The DNA probe that included the common G allele (lane 2) showed stronger protein binding than the DNA probe with the T allele (lane 6). Addition of unlabeled DNA showed the specificity of the band shift (lanes 1, 4, 5, and 8). The EMSA supershift was carried out by coincubation of an anti-Bach1 antibody with protein extract of gingival fibroblasts and DNA probes specific for the common G allele or the rare T allele of single-nucleotide polymorphism rs2012722. The effect T allele showed a weaker BACH1-AB supershift band compared to the noneffect G allele. (B) BACH1 binding affinity was 42% reduced in the background of the effect T allele compared to the noneffect G allele. (C) The band shift indicated BACH1 binding at rs3819872 (lanes 1–2, EMSA without BACH1 antibody). For the predicted BACH1 motif, the EMSA supershift was carried out by incubating an anti-Bach1 antibody with protein extract of gingival fibroblasts and specific DNA probes. The band supershift validated BACH1 binding at the predicted BACH1 transcription factor binding site (TFBS) (lane 4). (D, E) Reporter genes showed repressor activity of Region 1 (regulatory element tagged by rs3819872) and Region 2 (regulatory element tagged by rs2012722) in human immortalized fibroblasts 30 h after transfection independent of 6-h cigarette smoke extract (CSE) stimulation. (A) −CSE = −7.9-fold, P = 0.0228; +CSE = −5.8-fold, P = 0.0064. (B) −CSE = −1.9-fold, P = 0.0163; +CSE = −3.0-fold, P ≤ 0.0001. (F) Reporter gene plasmids with the repressor element (79 bp spanning rs2012722) showed reduced transcript levels compared to the control plasmid. The differences in reporter gene messenger RNA expression determined by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction were not significant between the individual alleles (P > 0.05).
