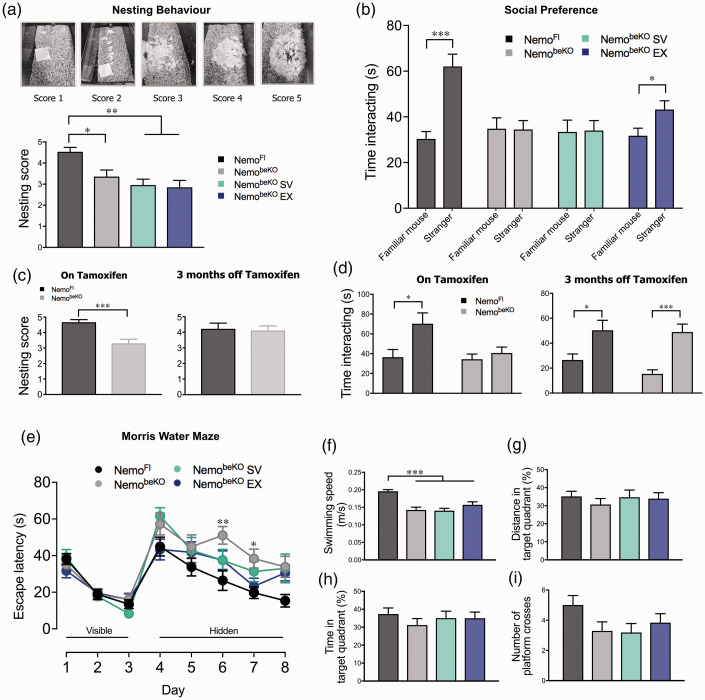
Figure 1.
NemobeKO groups had significantly lower nesting scores (a) and impaired social preference assessed by the 3-chamber sociability test (b). This same observation was made in NemobeKO mice injected with tamoxifen in the recovery cohort; however, after being given 3 months to recover, NemobeKO mice performed just as well as control NemoFl mice (c and d). Cognitive deficits observed on days 6 and 7 of the spatial learning phase of the Morris water maze (e) were attributed to decreased swimming speed that was recorded on each testing day for all groups. No deficits were detected during the spatial memory probe (f–i), trend in reduced platform crossings for NemobeKO groups regardless of treatment being attributable to impaired motor function evidenced by slower swimming speeds (f). Paired sample t-tests were performed for each group to compare time spent with individual mice for the sociability test. N = 12–15 mice/group, one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Newman-Keuls multiple comparison tests were performed for nesting behaviour and ANCOVA for Morris water maze performance controlling for swimming speed as the covariate. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.