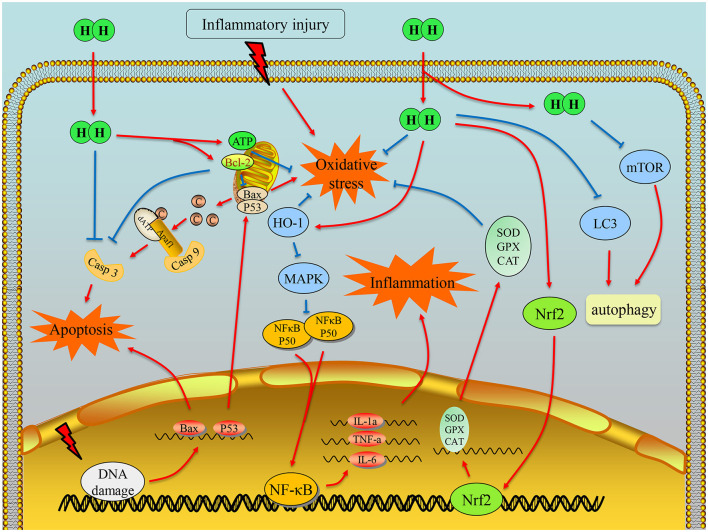
Figure 4.
Illustration of the main mechanism of hydrogen therapy in inflammatory diseases. First, hydrogen can scavenge hydroxyl radical due to its chemical property. It can also exert the antioxidation effects by regulating transcription of Nrf2 and energy balance of mitochondria. Moreover, hydrogen could downregulate the transcription of NF-κB, so that the inflammation can be alleviated. With the effects on antioxidation, anti-inflammation, and antiapoptosis factor Bcl-2 or direct interaction with caspase-3, hydrogen can inhibit cell apoptosis.