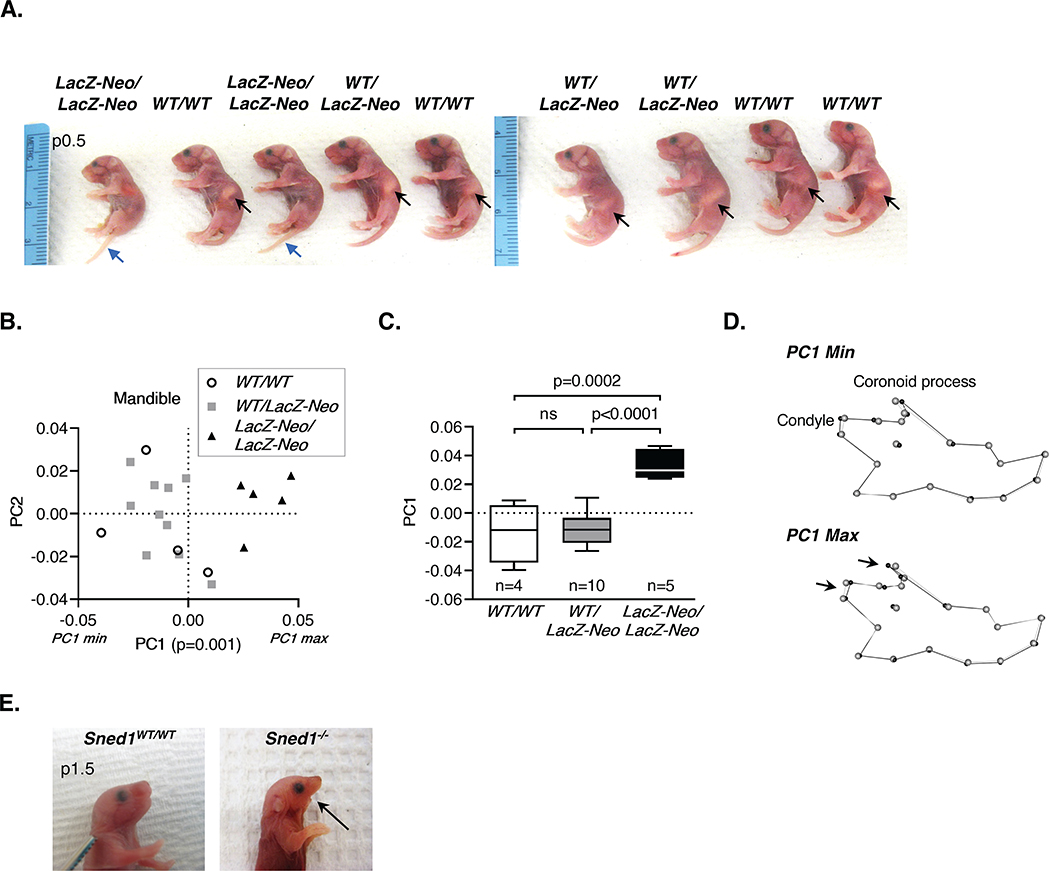
Figure 5. Sned1 knockout results in under-developed mandible.
A. Representative litter of p0.5 neonates. Black arrows indicate the presence of milk the stomach of wild-type and heterozygous mice. Note the absence of milk in the stomach of Sned1LacZ-Neo/LacZ-Neo neonates. Blue arrow points to the tails of knockout neonates which fail to curl, perhaps related to the strong expression in tail-bud somites and mesoderm (Figure 6).
B-D. Examination of the mandible of a cohort of 19 adult (6-month-old) global Sned1 knockout animals and control littermates.
B. Scatterplot of PC1 and PC2 for variation in the mouse mandibular morphology. Statistical analysis was performed using a one-way non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA.
C. Boxplot of mandibular PC1 data by mouse genotype. Numbers of mice per genotype are indicated. Statistical analysis was performed using a Tukey’s HSD test.
D. Wireframes depicting mouse mandible side view and variations as a function of genotypes. Grey dots represent the consensus cranium shape, and black dots represent the shape depicted by minimum (upper panel; representative of most Sned1WT/WT and Sned1WT/LacZ-Neo mice) and maximum (lower panel; representative of most Sned1LacZ-Neo/LacZ-Neo mice) PC1 range.
E. Pictures of a p1.5 wild-type (left panel) and age-matched dead Sned1−/− (right panel) neonates showing the absence of the lower jaw in the knockout pup.