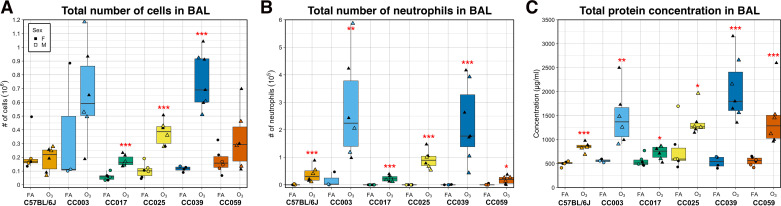
Figure 2.
O3 exposure causes variable inflammation and injury across six strains of mice. Total cellular inflammation (106; A), neutrophilia (105; B), and total protein concentration (μg/mL; C), a metric of lung injury, were measured in the BAL fluid. Data are presented as box-and-whiskers plots, which display the distribution from the minimum, first quartile, median, third quartile, and maximum. Individual data points are overlaid, with circles representing FA exposed mice and triangles representing O3 exposed mice. Females are closed points and males are open points. All measures had significant strain-by-O3 exposure interaction effects, assessed using a likelihood-ratio test (A: P < 0.0001, B: P < 0.05, C: P < 0.0001). (n = 3 mice per sex/treatment/strain except CC003 where n = 1 female/2 males exposed to FA and CC0039 where n = 4 females/3 males exposed to O3 and 3 females/1 male exposed to FA; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.0005, for within-strain contrasts (t tests) between FA and O3). BAL, bronchoalveolar lavage; FA, filtered air; O3, ozone.