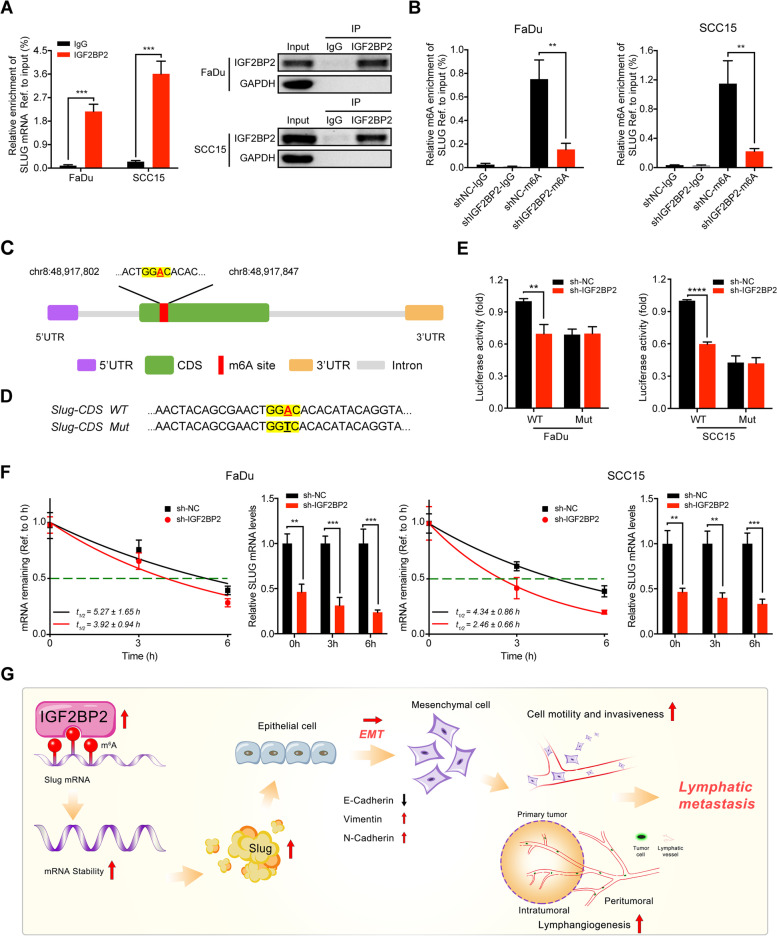
Fig. 7.
IGF2BP2 regulates slug mRNA stability via m6A modification. A RIP-qPCR analysis showing the enrichment of Slug mRNA in anti-IGF2BP2 precipitates (left panel). Western blot detected the IGF2BP2 immunoprecipitation efficiency of IGF2BP2 RIP assay in FaDu and SCC15 cells (right panel). GAPDH and IgG served as an internal or negative control, respectively. ***P < 0.001. B MeRIP-qPCR analysis showing the m6A enrichment of Slug mRNA using anti-IgG and anti-m6A antibodies in FaDu and SCC15 cells after silencing IGF2BP2. **P < 0.01. C A very high-confidence m6A site was identified in the CDS region upon Slug mRNA based on the SRAMP software analysis. D Schematic representation of Slug- WT (wild-type) or Slug- MT (mutated-type) sequence. E Luciferase reporter assays measured the luciferase activities of Slug-CDS WT or Slug-CDS Mut in FaDu and SCC15 cells with IGF2BP2 knockdown. **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001. F After silencing IGF2BP2 in FaDu and SCC15 cells, the mRNA half-lives and expression of Slug were analyzed at the predetermined times following actinomycin D (5 μg/ml) treatment. G A graphic illustration of the proposed mechanism in this study. In brief, IGF2BP2 was highly expressed in HNSCC patients, and recognized and bound to the m6A site upon Slug mRNA to maintain its mRNA stability and expression, thereby promoting cell migration and invasion through EMT progress, and leading to the lymphatic metastasis in HNSCC. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. All the data are presented in the form of mean ± SD from three independently performed experiments