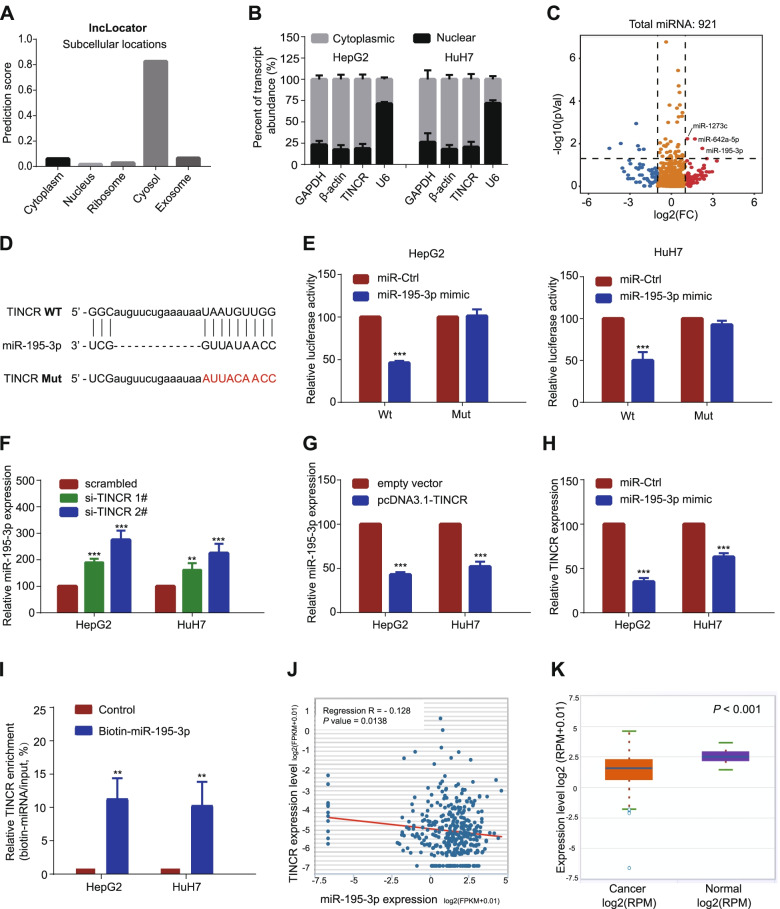
Fig. 4.
TINCR acts as a ceRNA and competitively absorbs miR-195-3p. A, TINCR was predicted to be located mainly in the cytosol using the bioinformatics tools in LncLocator. B, quantitative reverse transcription PCR analysis of TINCR expression in the nucleus and cytoplasm of HepG2 and HuH7 cells. GAPDH, β-actin, and U6 were used as endogenous controls. C, Volcano plots selected the significant up-regulated miRNAs in TINCR-silencing HCC cells (fold change > 1.5; P < 0.05). D, The predicted miR-195-3p binding sites in the TINCR transcript. The red nucleotides represent mutant sequences of target sites. E, The luciferase activities in HepG2 and HuH7 cells. F-G. Relative levels of miR-195-3p in HepG2 and HuH7 cells transfected with si-TINCRs or scrambled control (F), and pcDNA3.1-TINCR or empty vector (G). H, Relative levels of TINCR in HepG2 and HuH7 cells transfected with miR-195-3p mimic or miRNA control. I, Enrichment of TINCR pulled down by biotin-miR-195-3p or negative control. J, The relationship between levels of TINCR and miR-195-3p in HCC in starBase. K, MiR-195-3p was down-regulated in HCC compared to that in normal liver issues. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD of at least three independently repeated experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001