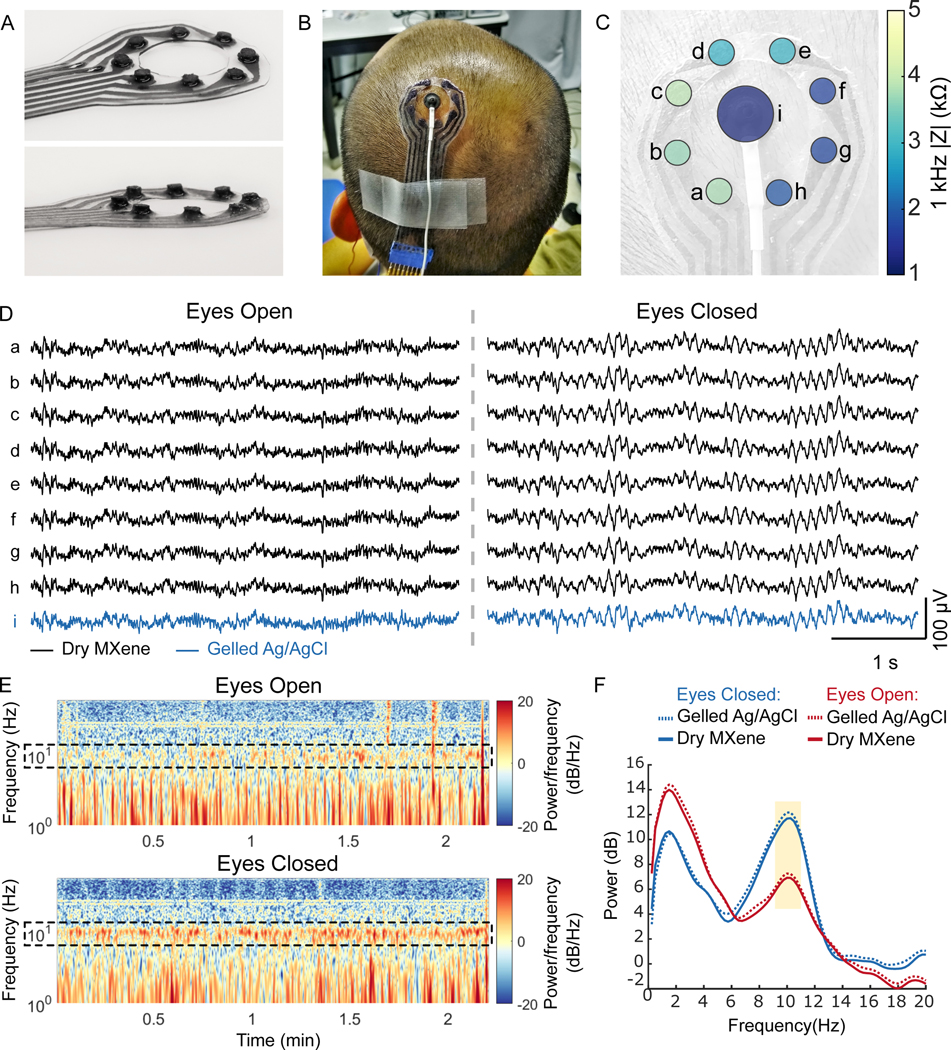
Fig. 3. Dry EEG recording enabled by 3D pillar MXtrodes.
(A) Photographs of a MXtrode 3D EEG array with eight 3 mm-diameter MXene electrodes in a circular arrangement around a central opening. (B) Photograph of MXtrode electrode array and standard gelled Ag/AgCl cup electrode placed on head of human subject. (C) Map of 1 kHz impedance values for all electrodes on the subject’s head. (D) Segments of recorded EEG signal from all electrodes during the eyes open (left) and eyes closed (right) tasks at resting state on one subject. (E) Spectrograms of the EEG signal recorded on MXene electrode b in the eyes open (top) and eyes closed (bottom) conditions. Alpha frequency band is enclosed in dashed box to highlight differences between eyes open and eyes closed states, which were consistent across 4 recording epochs. (F) Power spectral density during eyes open and eyes closed EEG recordings. The 8–12 Hz alpha band is highlighted.