Figure 6.
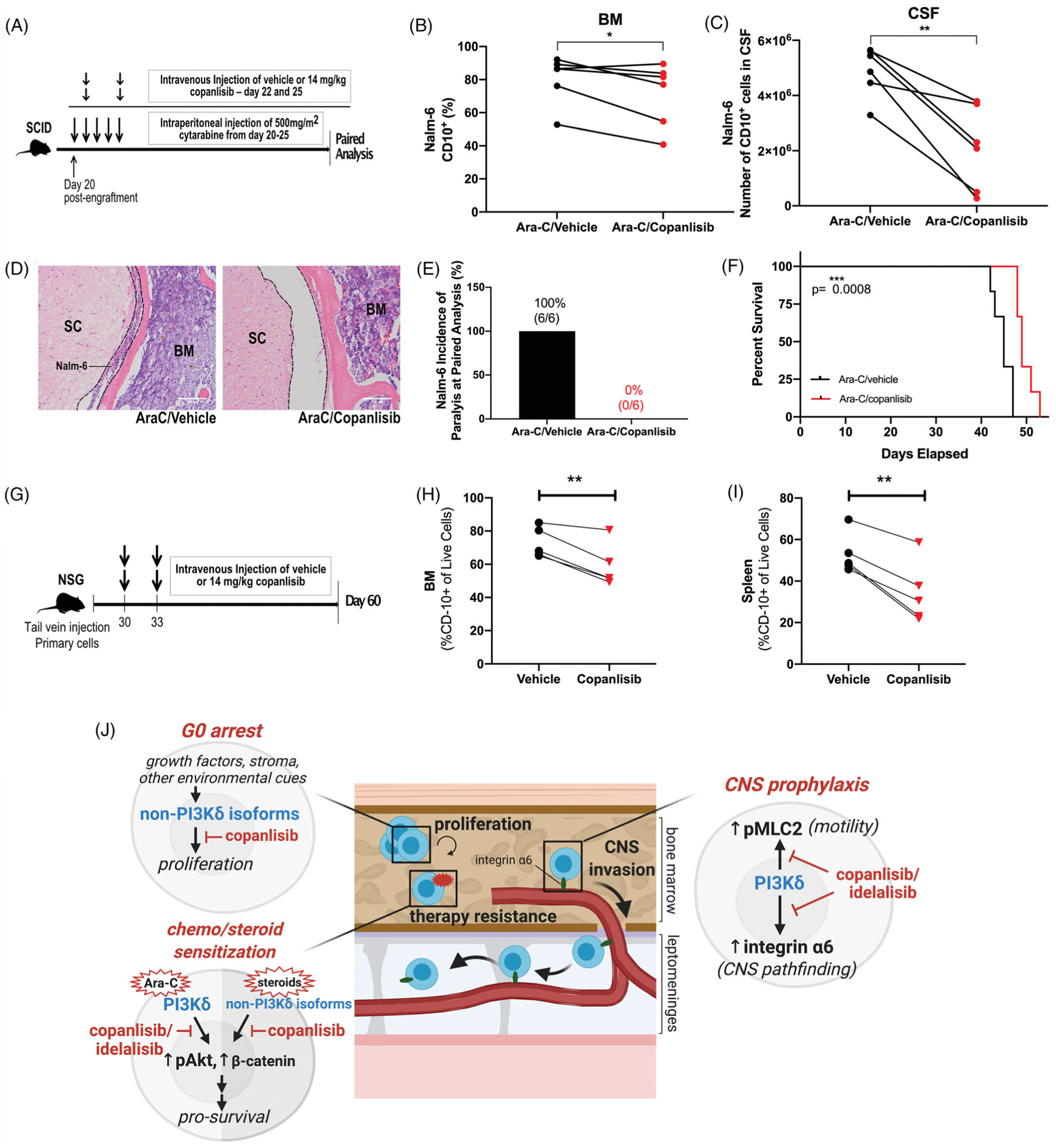
Copanlisib potentiates ALL to cytotoxic chemotherapy in vivo, resulting in increased survival as well as decreased BM and CNS disease. (A) Schematic of Ara-C/copanlisib treatment of leukemic mice. (B and C) Disease burden in the BM (percentage of CD10+ ALL cells) and in the CNS (number of CD10+ ALL cells) of Ara-C/vehicle and Ara-C/copanlisib-treated Nalm-6 engrafted mice euthanized at matched time points. Paired two-sided Student’s t-test, n = 6 mice per treatment group; p < 0.05, p < 0.01. (D) Nalm-6 ALL cells in subarachnoid space (dashed line) of the spinal cord (SC) at paired analysis following treatment with Ara-C/ vehicle and Ara-C/copanlisib. Representative sections of the vertebrae are shown. H&E, hematoxylin and eosin. n = 6 mice per treatment group. (E) Incidence of hind-limb paralysis in Ara-C/vehicle- and Ara-C/copanlisib-treated Nalm-6 engrafted mice at paired analysis. (F) Kaplan-Meier survival curve of Nalm-6 (GFP) engrafted SCID mice treated with Ara-C/vehicle or Ara-C/copanlisib. Two-sided log rank Mantel-Cox test, n = 6 mice per group, p < 0.001. (G) Schematic of copanlisib treatment of PDX leukemic mice. (H–I) Disease burden in the BM and spleen (percentage of CD10+ ALL cells) of vehicle and copanlisib treated primary B-ALL engrafted NSG mice at day 60. Paired two-sided Student’s t-test, n = 5 mice per treatment group; p < 0.01 (J) Model of PI3Ki action in B-ALL: PI3K-dependent ALL cell proliferation in the BM is predominantly mediated by PI3Kα/β/γ isoforms, with pan-PI3K inhibition via copanlisib leading to a G0 cell cycle arrest. PI3Kδ and PI3Kα/β/γ signaling activate Akt-dependent pro-survival pathways conferring resistance to chemotherapy or steroids respectfully. Lastly, PI3Kδ signaling leads to the upregulation of integrin α6 and the activation of MLC2-dependent motility, allowing for invasion along laminin+emissary vessels that passage from the calvarial and vertebral BM into the leptomeninges.
