Figure 6.
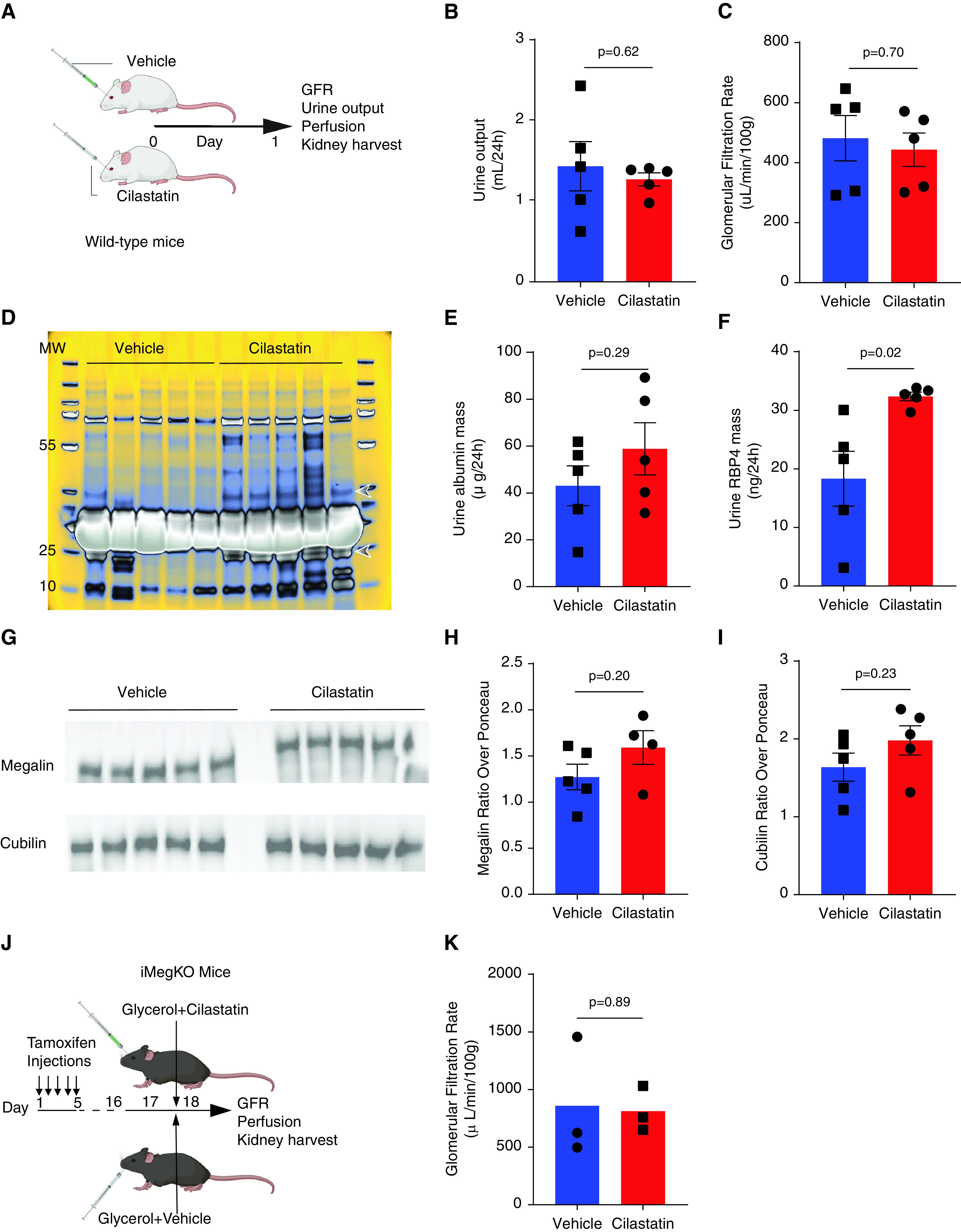
Cilastatin and megalin deletion have similar effects on renal function. (A) Experimental design for results (B–I). Wild-type mice received cilastatin (200 mg/kg) or vehicle injection as in prior experiments, without injection of glycerol. The 24 hours later, outcomes were assessed. (B and C) Urine output and GFR were not altered by cilastatin administration. (D) Coomassie-stained urine electrophoresis (loaded with identical volumes of urine from each animal). Bands at approximately 23 kD and approximately 40 kD marked by arrowheads appear differentially expressed in cilastatin versus vehicle samples. The same bands may be seen in the urine of iMegKO mice in Figure 1. Unaltered gel image shown in pseudo-color to better visualize peak protein density. (E) Urine albumin was not significantly increased. (F) RBP4, a plasma protein that is a known megalin ligand, and is greatly increased in the urine of megalin-deleted mice, was nearly doubled by cilastatin administration. (G–I) Immunoblots performed on kidney lysate 24 hour after vehicle or cilastatin injection. Megalin expression was reduced after cilastatin administration, whereas cubilin was not significantly altered. (J) Experimental design. iMegKO mice received cilastatin or vehicle with injection of glycerol. Then 24 hours later, mean GFR was identical between groups (K), indicating that cilastatin-dependent protection from rhabdomyolysis-induced AKI is absent in mice without proximal tubule megalin. Statistical analysis presented is derived from the t test.
