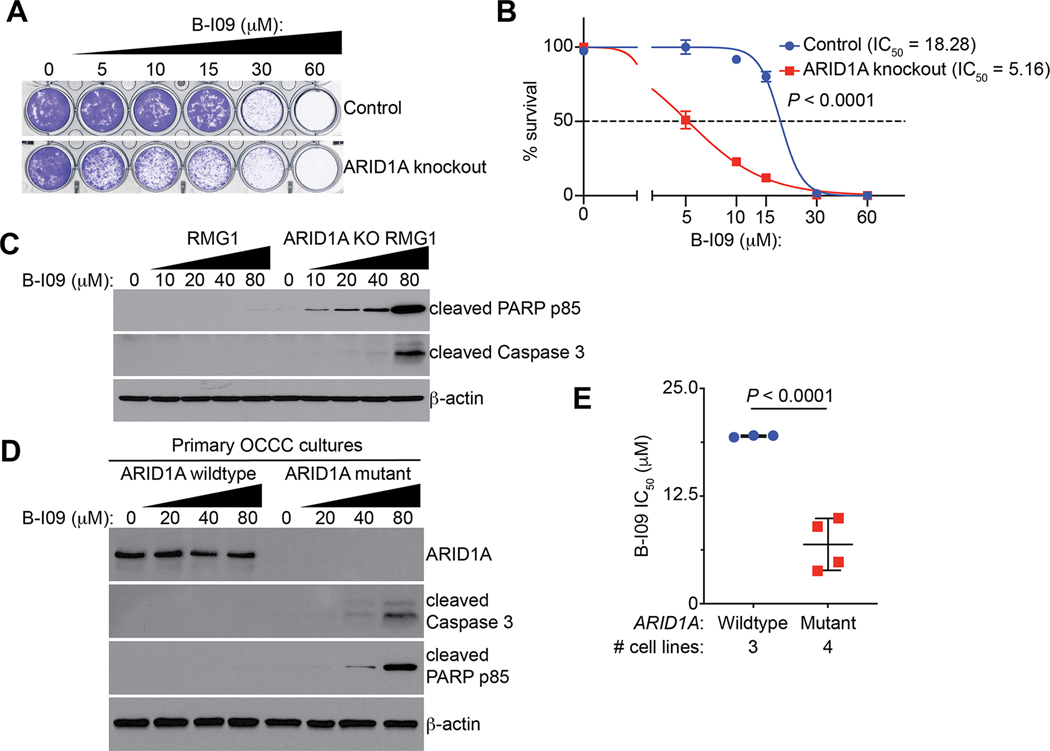
Figure 3: ARID1A inactivation sensitizes cells to IRE1α inhibition.
(A) Representative images of colony formation assay in control and ARID1A knockout RMG1 cells treated with indicated concentrations of B-I09. (B) Dose-response curves of indicated control and ARID1A knockout RMG1 cells to B-I09 were determined by colony formation assay. n = 4 biologically independent experiments. (C) Control and ARID1A knockout RMG1 cells were treated with the indicated doses of B-I09 for 24 hours. Expression of the indicated markers of apoptosis and a loading control β-actin was examined by immunoblot. (D) ARID1A wildtype and mutant primary OCCC cultures were treated with the indicated concentration of B-I09 for 24 hours. Expression of ARID1A, the indicated markers of apoptosis and a loading control β-actin was determined by immunoblot. (E) IC50 of B-I09 is significantly higher in ARID1A wildtype (RMG1, OVCA429 and KK) than mutant (TOV21G, OVTOKO, OVISE and SKOV3) cell lines. P values were calculated using two-tailed Student’s t-test. Error bars represent mean with SD.