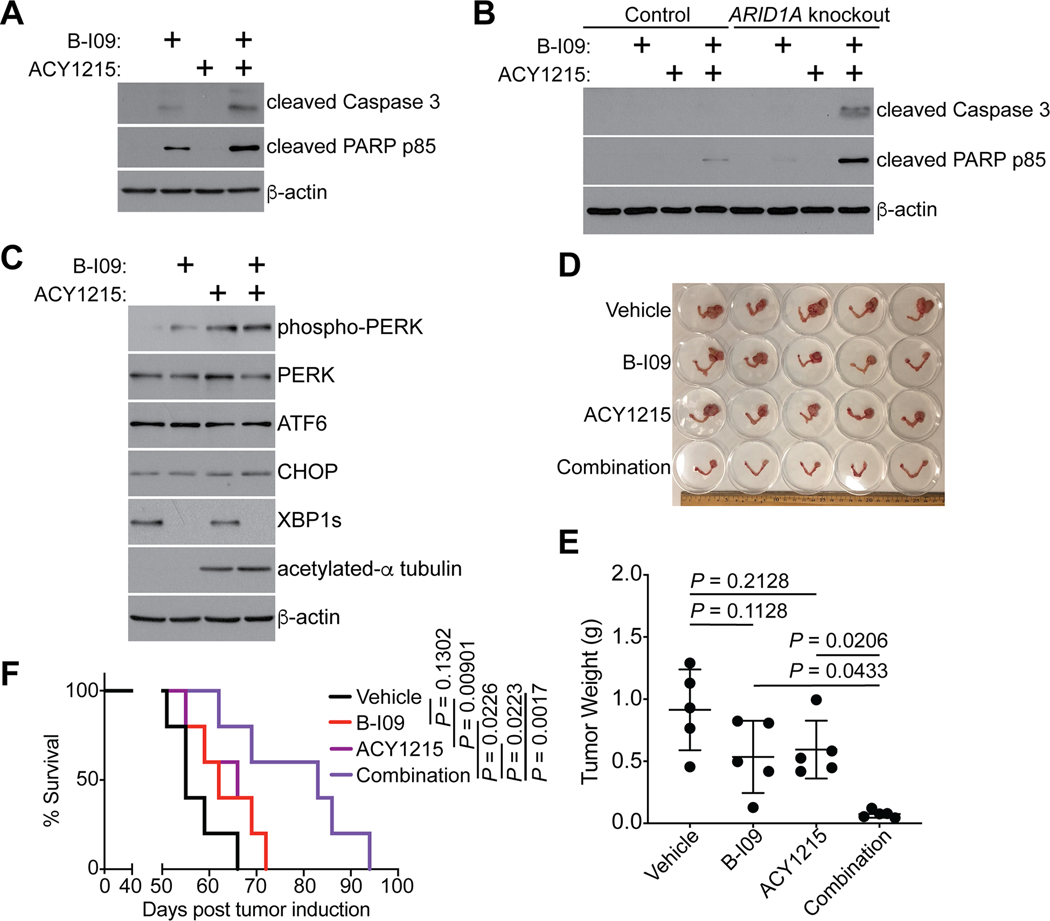
Figure 6: IRE1α and HDAC6 inhibitors are synergistic in suppressing ARID1A-inactivated OCCCs.
(A) ARID1A-mutated TOV21G cells were treated with the IRE1α inhibitor B-I09 (20μM), HDAC6 inhibitor ACY1215 (3 μM), or a combination for 72 hours. Expression of the indicated apoptosis markers and a loading control β-actin was examined by immunoblot. (B) Same as (A), but for control and ARID1A knockout RMG1 cells. (C) ARID1A-mutated TOV21G cells were treated with the IRE1α inhibitor B-I09 (20μM), HDAC6 inhibitor ACY1215 (3 μM), or a combination for 72 hours. Expression of the indicated apoptosis markers and a loading control β-actin was examined by immunoblot. (D-F) Mice bearing OCCCs developed from the genetic Arid1a−/−/Pik3caH1047R model were treated with B-I09 (25 mg/kg), ACY1215 (25 mg/kg) or a combination for 3 weeks (n = 5 mice per group). Shown is an image of reproductive tracks with tumors from the indicated groups at the end of treatments (D). Tumor weight was measured as a surrogate for tumor burden (E). After stopping the treatment, mice from the indicated treatment groups were followed for survival by the Kaplan-Meier methods (n = 5 mice per group) (F). P values were calculated using two-tailed Student’s t-test in D and log-rank test in F. Error bars represent mean with SD.