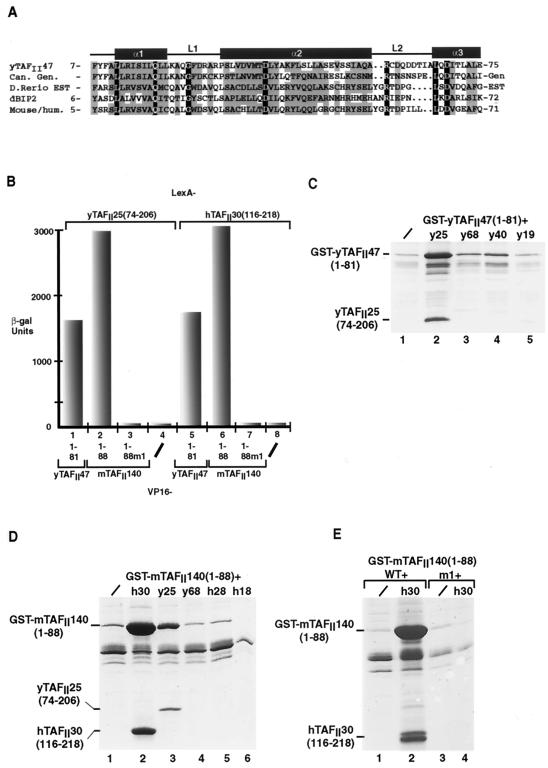
FIG. 1.
Functional analysis of the HFD from a putative mouse and human yTAFII47 homologue. (A) Alignment of the HFD sequence of yTAFII47 with those of its putative Candida albicans (Can), zebrafish (Danio rerio), Drosophila melanogaster (dBIP2), and human and mouse homologues. The positions of the predicted α-helices and loops are indicated above the sequences. Identical amino acids are shown in white letters on a black background. Positions with conserved, mainly hydrophobic amino acids are boxed in gray. Amino acids were classified as follows: small residues, P, A, G, S, T; hydrophobic residues, L, I, V, A, F, M, C, Y, W; polar and acidic residues, D, E, Q, N; basic residues, R, K, H. Threonine residues are occasionally present in otherwise hydrophobic positions. The amino acid sequences shown without numbers are predicted from genomic (gen) or EST sequences. The accession numbers for the indicated sequences are as follows: C. albicans, 396380B03; zebrafish, GenBank accession no. AW343321fi76b06.y1; Drosophila BIP2, Q9XZU7; mouse, GenBank accession no. AA692266ur52c07. (B) Graphical representation of quantitative two-hybrid β-galactosidase assays. The LexA chimeras shown above the graph were tested with the VP16 chimeras shown below each column. −, negative controls with the VP16 domain alone. (C, D, and E) Coexpression of the yTAFII47 and mTAFII140 HFDs with those of other TAFIIs in E. coli cells. Bacteria were transformed to express the proteins shown above each lane, and following extract preparation, the soluble protein retained on glutathione-Sepharose beads was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and staining with Coomassie brilliant blue. /, GST-fusion was expressed alone. The locations of the GST-yTAFII and GST-mTAFII fusions and the retained yTAFII25 and hTAFII30 proteins are indicated.