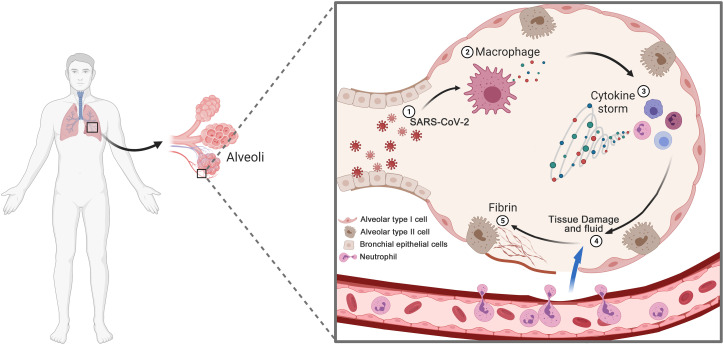
Fig. 3.
Schematic diagram of cytokine storm in COVID-19. (1) SARS-CoV-2 infects lung bronchial, alveolar type I and type II epithelial cells. (2) Immune cells, including macrophages, recognise viruses and produce cytokines. (3) Cytokines attract more immune cells, such as neutrophils, T cells, monocyte and DCs, which in turn produce more cytokines, creating a cycle of inflammation that damages the lung cells. (4) Persistent inflammation lead to tissue damage, leucocytes infiltration and fluid leakage from the blood vessel, causing respiratory failure. (5) Excessive deposit of fibrin in the lungs.