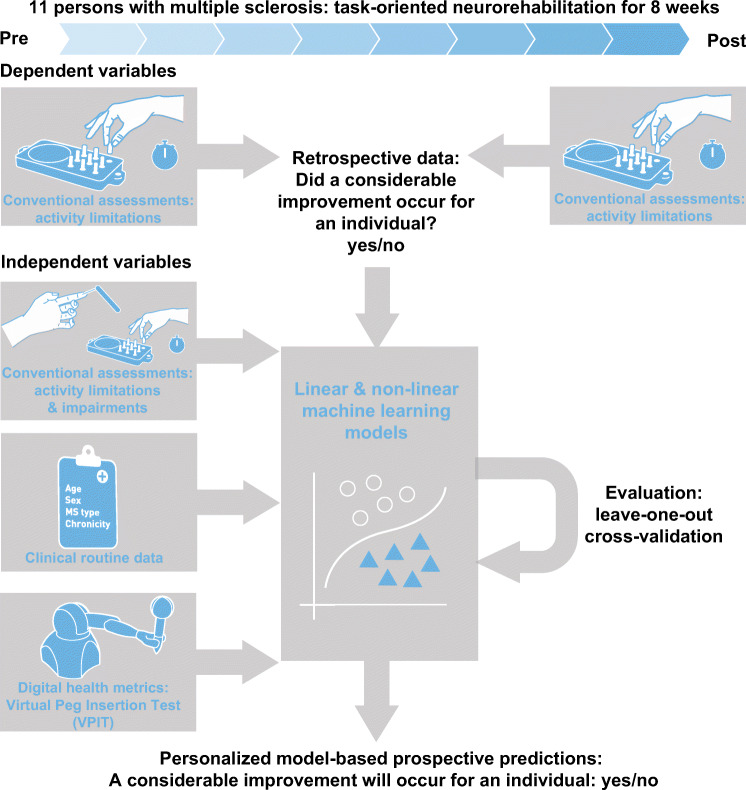
Fig. 1.
Approach for prediction of neurorehabilitation outcomes in persons with multiple sclerosis. Eleven persons with multiple sclerosis were assessed before and after eight weeks of neurorehabilitation. Multiple linear and non-linear machine learning models were trained on different feature sets with data collected before the intervention. This included information from conventional clinical assessments about activity limitations and impairments, clinical routine data, and digital health metrics collected with the Virtual Peg Insertion Test (VPIT). The dependent variable of the models defined whether a considerable improvement in activity limitations occurred across the intervention or not. The quality and generalizability of the models were evaluated in a leave-one-subject-out cross-validation