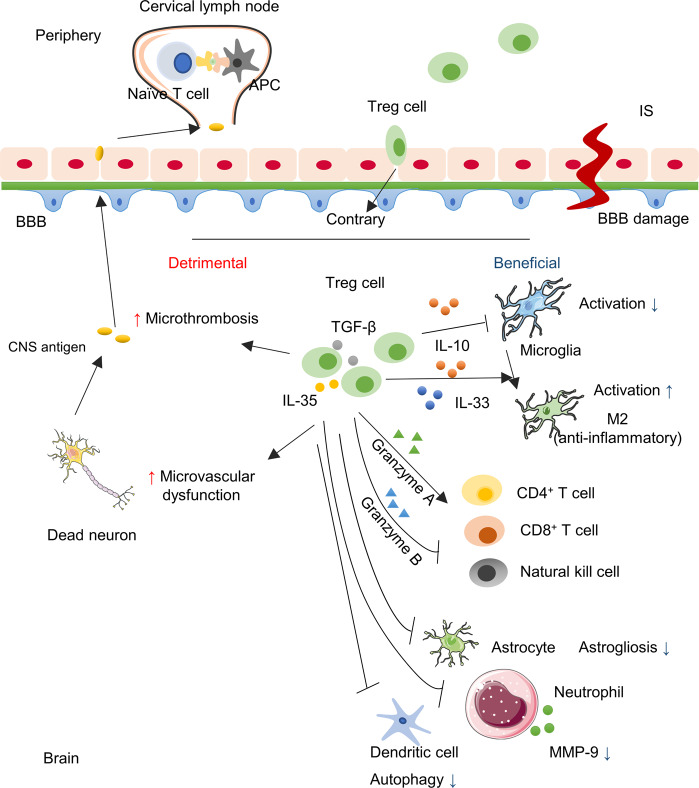
Fig. 1. The role of Treg cells in ischemic stroke.
Ischemic stroke leads to the damage of the BBB and neuron cells. The CNS antigen would be generated, pass the BBB and drain to the peripheral lymphoid nodes where they are taken up by APCs and further presented to naïve T cells. Treg cells as crucial immunomodulators, are transferred into the brain and exert a neuroprotective effect through the cytokine-dependent pathway via IL-10, IL-33, etc. Moreover, Treg cells modulate effector cells through the granzyme-dependent pathway, the crosstalk with several other cells, and the inhibition of neutrophil-derived MMP-9. However, Treg cells can be detrimental to cerebral injury with microthrombosis and microvascular dysfunction.